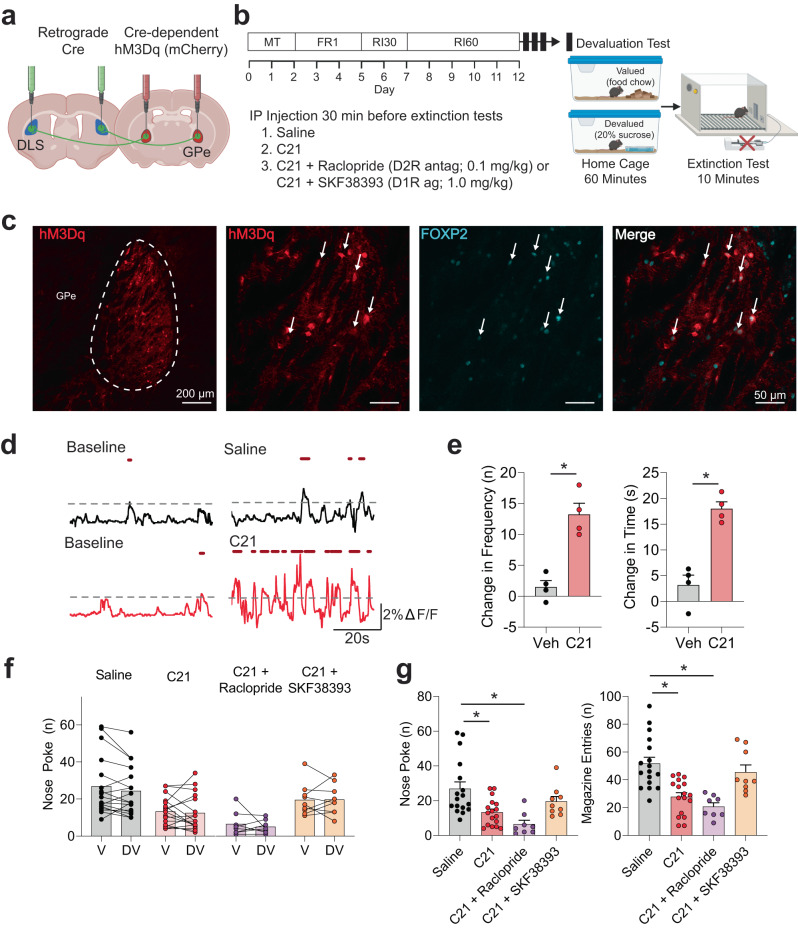
Fig. 5. Effects of chemogenetic activation of external globus pallidus (GPe) arkypallidal neurons on habitual reward-seeking.
a Schematic of virus injection strategy for Cre-dependent expression of the excitatory DREADDs hM3Dq. b RI operant schedule followed by evaluation tests with IP injection groups. c Representative images showing hM3Dq expression in the GPe and coexpression with arkypallidal neuron marker FOXP2 from n = 3 mice. Scale: 200 µm (left), 50 µm (rest). d Representative calcium traces for hM3Dq-expressing GPe arkypallidal neurons at baseline and following C21 or vehicle administration in freely moving mice. e C21 administration caused a notable increase in the frequency and duration of Ca2+ events (frequency: t = 4.47, p = 0.021, time: t = 11.86, p = 0.0013). n = 4 mice/group. f There were no differences between the valued and devalued states for IP injection treatment. g The effects of DREADDs activation and IP injection groups on nose poke and magazine-entry seeking behaviors during the extinction test. Noke poke with drug treatment (p = 0.0004), z = 2.71, p = 0.04 for saline versus C21, z = 3.96, p = 0.0005 for saline versus C21+Raclopride, z = 0.83, p = 0.99 for saline versus C21 + SKF383393. Magazine entry with drug treatment (p < 0.00001), z = 3.59, p = 0.002 for saline versus C21, z = 4.13, p = 0.0002 for saline versus C21+Raclopride, z = 0.69, p = 0.99 for saline versus C21 + SKF383393. Two-tailed t tests were used for (e). Wilcoxon test was used for (f). Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s posthoc tests were used for (g). n = 17 (Saline, C21), 8 (C21 + Raclopride), 9 (C21 + SKF38393) for (f, g). Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. See Supplementary Table 2 for full statistical information. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. (a, b) were created with BioRender.com.