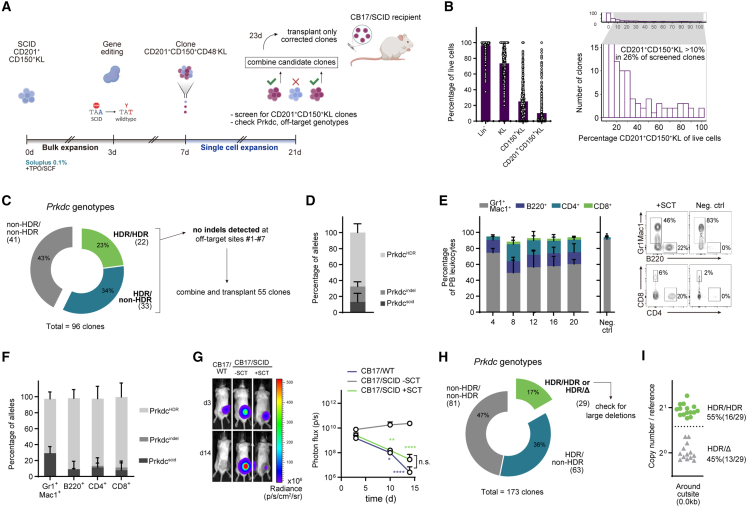
Figure 5.
Autologous HSCT using gene-corrected HSC clones is curative in an immunodeficiency mouse model
(A) Schematic of the single clone Prkdcscid correction model.
(B) Single-cell SCID HSC expansion outcomes. Left: frequencies of phenotypic HSC populations in screened colonies (n = 384 from 3 experiments). Right: histogram of CD201+CD150+KL cell frequency. Enlarged region shows clones with ≥10% CD201+CD150+KL cells.
(C) Genotyping of candidate clones (Sanger sequencing) (n = 96 clones, 3 experiments). Only clones with at least one HDR-corrected allele were sequenced at the off-target loci.
(D) Allelic composition of the combined cell mixture at the edited Prkdc locus (n = 3).
(E) Frequencies of PB leukocytes in CB17/SCID recipients. Left: lineage distributions in treated mice (n = 3) and in recipients receiving only 2 × 105 CB17/SCID whole bone marrow cells (neg. ctrl., n = 3). Right: representative FACS plots at 16 weeks post-SCT.
(F) Allele frequencies in sorted PB cells 20 weeks post-SCT (n = 3 mice from 3 experiments).
(G) Xenograft transplantation assay. A549 cells expressing the luminescent reporter Akaluc were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) and tumor growth was tracked by in vivo imaging. Left: representative images from CB17/WT, transplanted CB17/SCID, and untreated CB17/SCID mice 3 and 14 days after inoculation. Right: quantification of luminescence over a 14-day period (CB17/WT: n = 4, CB17/SCID − SCT: n = 3, CB17/SCID + SCT: n = 3). Two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(H) Genotyping of candidate clones (Sanger sequencing) (n = 173 clones, 2 experiments). Clones producing a single, HDR-corrected sequencing trace were checked for LD (n = 29). PrkdcHDR/HDR, homozygous correction; PrkdcHDR/Δ, hemizygosity.
(I) Prkdc copy-number analysis using 0.0 kb Prkdc (around cutsite) probe, quantified against reference gene.
See also Figure S5.
Error bars represent SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.