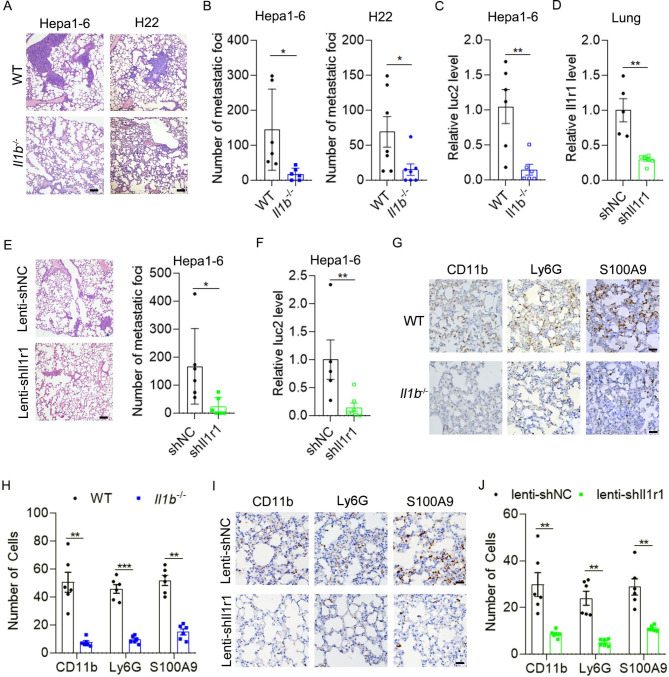
Fig. 3.
IL-1β/IL-1R1 signaling promotes the pre-metastatic niche formation and pulmonary metastasis of HCC xenografts. (A-C) Pulmonary metastases of HCC xenografts were reduced in Il1b−/− mice. Hepa1-6 cells (A and B, left panel, and C) or H22 cells (A and B, right panel) were implanted orthotopically in the liver of WT and Il1b−/− mice, and pulmonary metastases were detected 4 weeks or 3 weeks later by H&E staining, respectively. Scale bar, 100 μm. For (C), pulmonary metastasis was detected by qPCR analysis of luc2. (D) Intratracheal administration of lenti-shIl1r1 viruses decreased Il1r1 mRNA level in the lung. (E-F) Silencing of Il1r1 in the lung decreased pulmonary metastases of HCC xenografts. For (D-F), lenti-shCtrl or lenti-shIl1r1 viruses were given intratracheally to the lung of WT mice. After 3 days, mice were orthotopically injected with Hepa1-6 cells. Il1r1 mRNA level and pulmonary metastases were detected 4 weeks later. Pulmonary metastasis was detected by H&E staining (E) and qPCR analysis of luc2 (F), respectively. (G-J) Accumulation of myeloid cells and inflammatory cells in the pre-metastatic lung was suppressed in Il1b−/− mice (G-H) and mice infected with lenti-shIl1r1 viruses in the lung (I-J). For (G-J), two weeks after orthotopic implantation of Hepa1-6 cells, mice were sacrificed and IHC staining of CD11b+, Ly6G+ and S100A9+ cells in the lung were performed. Scale bar, 25 μm. Data are displayed as the mean ± SEM; unpaired Student’s t test (B-F, H and J). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001