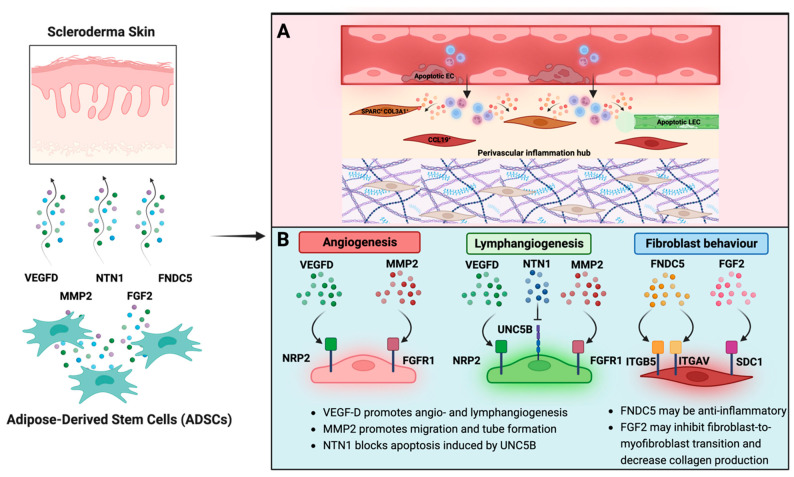
Figure 8.
Summary of possibly therapeutic interactions of ADSCs with fibroblasts and endothelial cells from scleroderma. (A) Single-cell analyses of chronic inflammatory diseases [9] and scleroderma [8] identified a proinflammatory CCL19+ and a SPARC+/COL3A1+ fibroblast subset that colocalises with the vasculature, highlighting the importance of the perivascular inflammation hub for activation of fibroblasts in scleroderma. (B) Based on differences and commonalities in cell-to-cell receptor–ligand interactions of ADSCs with fibroblasts and endothelial cells from healthy and scleroderma skin, VEGFD, MMP2, NTN1, FNDC5, and FGF2 were identified as possible anti-fibrotic effector molecules. Created with BioRender.com.