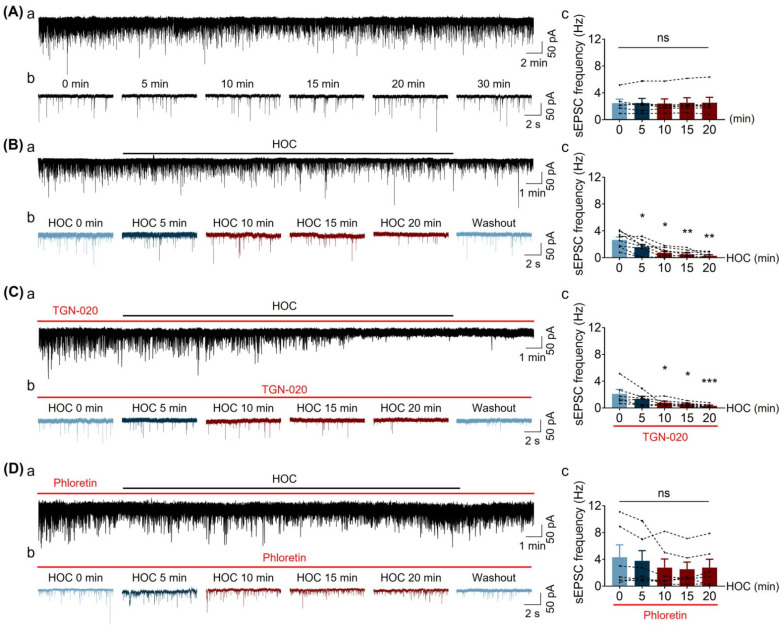
Figure 3.
Effect of TGN-020 or phloretin on spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current (sEPSC) frequency of VP neurons during HOC in acute SON slices. (A). Representative sEPSCs from VP neurons at rest recorded in the whole-cell voltage clamp mode in continuous recording ((a), Vh= −70 mV) or in recording episodes (b) and summary of average sEPSC frequency ((c), n = 6; ANOVA, Bonferroni). (B). sEPSCs from VP neurons at various time points of HOC in continuous recording or in recording episodes (a,b), respectively and summary of average sEPSC frequency ((c), n = 8; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with 0 min HOC; ANOVA, Bonferroni). (C). sEPSCs from VP neurons at various time points during HOC (a,b) and summary of average sEPSC frequency ((c), n = 6; *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.005 compared with 0 min; ANOVA, Bonferroni) in the presence of 10 μmol/L TGN-020. (D). sEPSCs from VP neurons at various time points during HOC (a,b) and summary of average sEPSC frequency ((c), n = 6; ANOVA, Bonferroni) in the presence of 30 μmol/L phloretin. Total duration of each recording from individual cells in (A)a, (B)a, (C)a, and (D)a is 40 min. Abbreviations: sEPSC, excitatory postsynaptic currents; ns, non-significant. For other annotations and abbreviations, refer to Figure 1.