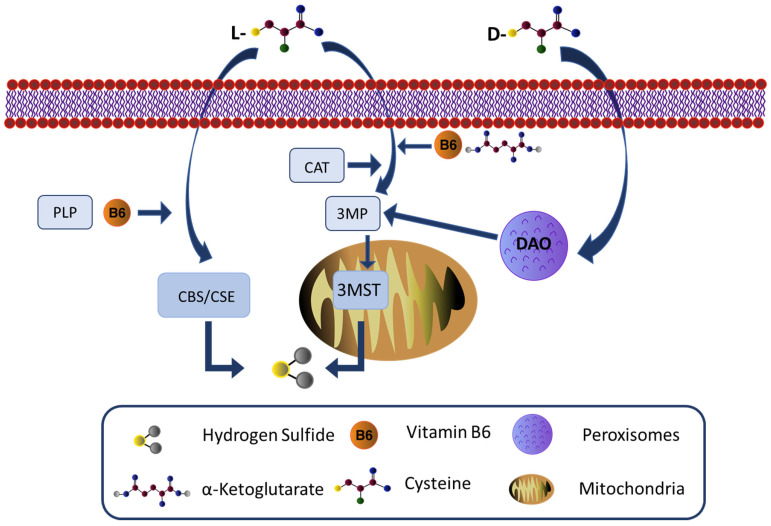
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of hydrogen sulfide production. Endogenously, H2S is produced by three enzymes: cystathionine-beta-synthase (CBS), cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE), and cysteine aminotransferase (CAT)/3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST). It has also been reported that it can be produced in brain homogenate when D-cysteine is added instead of L-cysteine. CBS, CSE, and CAT enzymes require pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor and all use L-cysteine as a substrate which is a by-product of L-methionine, homocysteine, and cystathionine. 3-mercaptopyruvate is converted from cysteine by the action of cysteine aminotransferase. As a semi-essential amino acid, cysteine can be obtained from alimentary sources or liberated from the catabolism of endogenous proteins. 3MST uses 3 mercaptopyruvate (3MP), generated by CAT from L-cysteine and a-ketoglutarate (a-KG), in association with vitamin B6 as a substrate to produce H2S. Both enzymes have a cytosolic and a mitochondria isoform. The mitochondria subcellular isoform is probably the relevant one, since it is where cysteine is preferentially found. Finally, D-Amino acid oxidase (DAO), which is localized to peroxisomes, can produce 3MP through the oxidative deamination of D-cysteine. 3MST can produce H2S along with DAO, exploiting the interaction between those organelles, normally in close proximity and known to exchange metabolites.