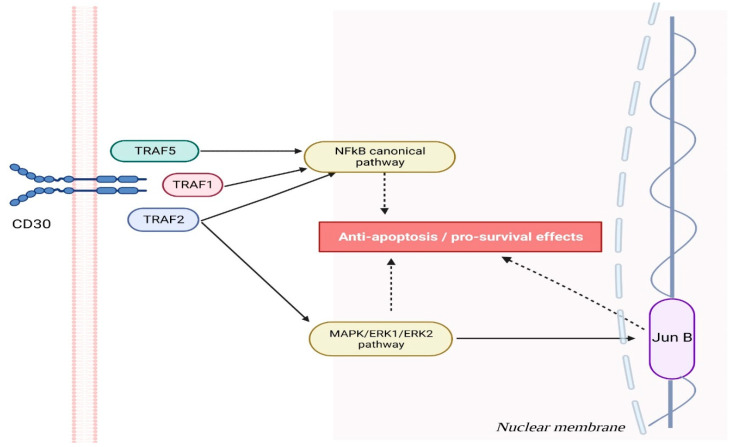
Figure 1.
The CD30 molecule plays a critical role in cell survival by engaging various signaling pathways that confer an advantage to cells with higher CD30 levels. When activated, CD30 forms trimers and sends out signals through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated proteins (TRAF), specifically TRAF2, TRAF1, and TRAF5, to stimulate nuclear factor-kappa B (NFkB) pathways and thus increase survival chances. CD30 binding initiates signaling through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, including ERK1 and ERK2, that activate mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase. This provides cancerous cells with various anti-apoptotic and pro-survival benefits, with JunB acting as a nuclear transcription factor to further support survival while upregulating CD30 expression.