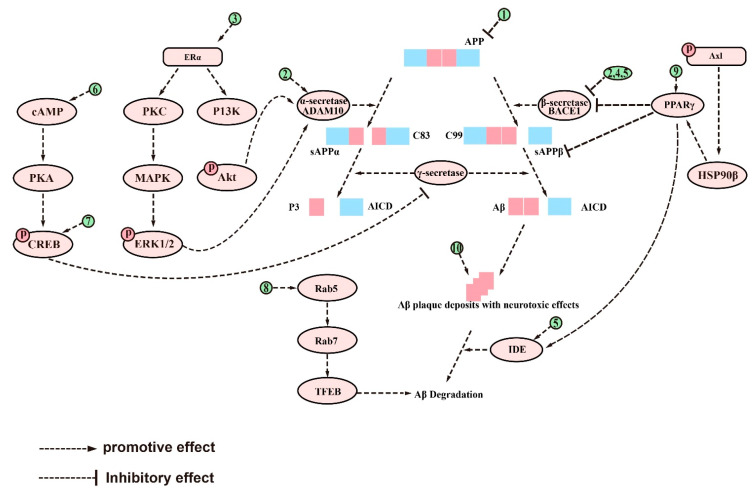
Figure 2.
The signaling pathways and targets of Aβ metabolism regulation by saponins. (1). Ginsenoside Rg1 and xanthoperidinol, to inhibit Aβ formation by reducing APP production; (2). Ginsenoside Rg1 and theasaponin E1, can enhance α-secretase activity and decrease β-secretase and γ-secretase activity; (3). Ginsenoside Rg1, regulates targets of PKC, MAPK, and PI3Ksignaling pathways; (4). RAPO-1-3, onjisaponin B, and PF11, can decrease β-secretase activity; (5). CK, can reduce the expression of BACE1 and PS1 and increase the activity of IDE; (6). Ginsenoside Rg1, regulates targets of PKA/pCREB signaling pathways; (7). Minor ginsenoside F1, can enhance the expression of pCREB; (8). PF11, can recover Rab conversions; (9). Ginsenoside Re, NTR1, AS-IV, Jujuboside A, and ginsenoside Rg1, regulate targets of PPARγ signaling pathways; (10). Hederacolchiside-E, polanoside A, chikusetsu saponin V, NTR1, and Akquintoside F, can directly inhibit the neurotoxicity of Aβ. The above-mentioned saponins inhibit the metabolism of Aβ by modulating the targets of these signaling pathways.