Figure 7.
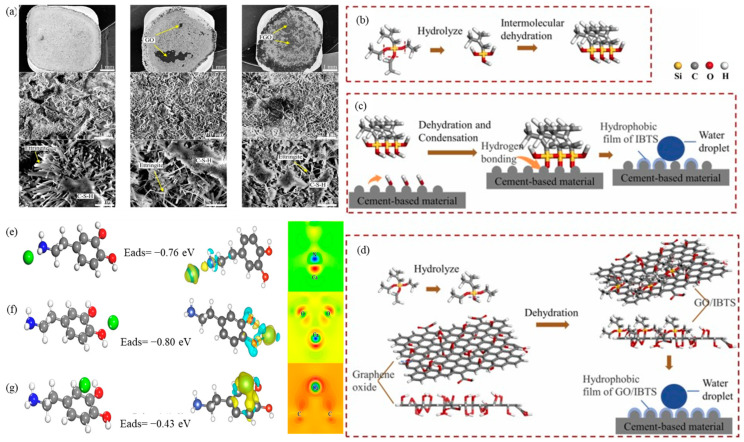
(a) SEM images were used to compare the microstructures of (left) the control sample, (middle) GO-containing cement complex, and (right) FGO-containing cement complex. Needle-like crystals (ettringite) were observed in all three samples, but the FGO-containing complex had fewer and smaller crystals. Additionally, the pore size decreased in the order: control sample > GO-containing complex > FGO-containing complex [68]. The scale of the top, middle and bottom columns are 1mm, 10 μm, and 2 μm respectively. Adapted from Ref. [68]. Copyright 2020 John Wiley and Sons. The concrete surface becomes hydrophobic after silane treatment, achieved by the GS composite emulsion mechanism; (b) IBTS hydrolysis forms Si-OH and Si-O-Si bonds; (c) Si-O-Si bonds undergo dehydration and condensation forming a hydration product with OH bonds, leading to hydrogen bond formation and hydrophobic films, and (d) Si-OH bonds interact with -OH groups of GO, resulting in a thicker, denser hydrophobic layer [103]. Adapted from Ref. [103]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier. Dopamine (DA) enhances interfacial bonding on concrete by inducing ion mineralization on its surface. DFT analysis reveals three stable structures of DA molecules on Ca2+ with varying adsorption and charge densities. These structures involve Ca2+ adsorbed on (e) nitrogen, (f) oxygen atoms of hydroxyl groups, and (g) carbon rings with different bond lengths. The second structure, which closely resembles the Ca-O bond length in CaO crystals, is the most stable due to its low adsorption energy. Electron accumulation is depicted in yellow, while electron depletion is shown in blue [3]. Adapted from Ref. [3]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier.