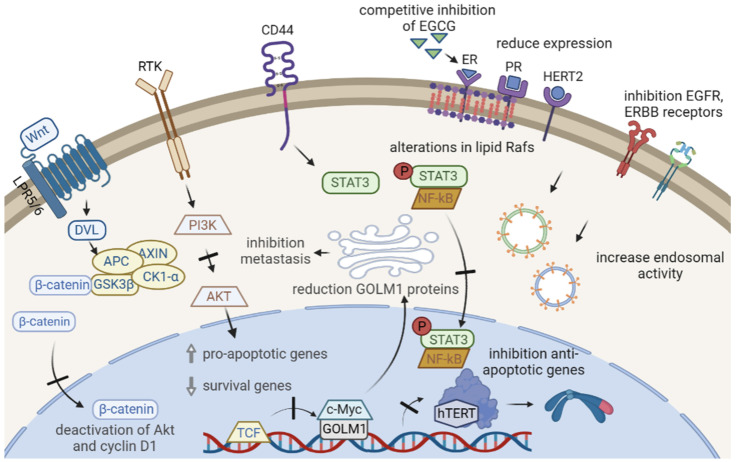
Figure 2.
Multiple effects of EGCG in breast cancer. EGCG inhibits phosphorylation and activation of signaling pathways such as β-catenin, PI3K/AKT, and STAT3, preventing the translocation of its effectors to the nucleus. The main effect of this is the promotion of apoptosis and the inhibition of anti-apoptotic genes. In addition, this causes a decrease in the gene expression of the catalytic subunit of the telomerase enzyme hTERT. EGCG can act as a competitive inhibitor of hormones such as estradiol at key receptors for tumor growth, decrease its surface expression, alter its dispositions on the surface due to changes in lipid Rafts, or increase endosomal activity in the cell.