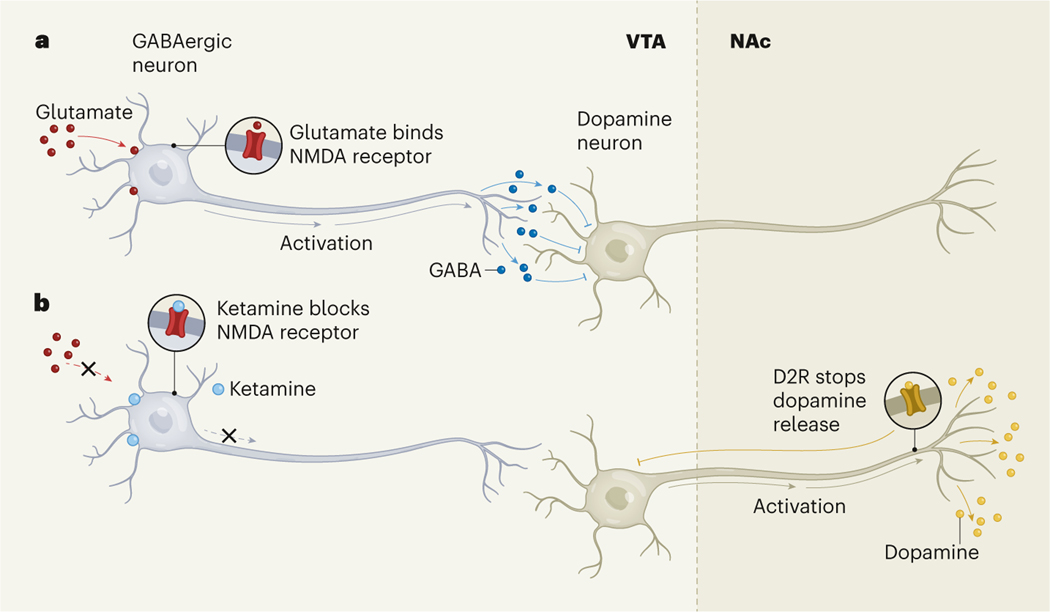
Figure 1 |. The effects of ketamine on dopamine release.
a, GABAergic neurons in the brain’s ventral tegmental area (VTA) are stimulated by binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to NMDA receptor proteins. These neurons release the neurotransmitter GABA, which inhibits the activity of dopamine neurons that project to a reward centre called the nucleus accumbens (NAc). b, Ketamine binds to NMDA receptors to inhibit their activation. Simmler et al.3 show that this leads to activation of the dopamine neurons, triggering a short burst of dopamine release in the NAc. The release is rapidly quashed when dopamine binds to the D2-type receptor (D2R) protein on the dopamine neurons, inhibiting their activity. This mechanism of action differs from the pathways through which cocaine triggers sustained dopamine release (not shown), which might explain why ketamine is not highly addictive.