Figure 2.
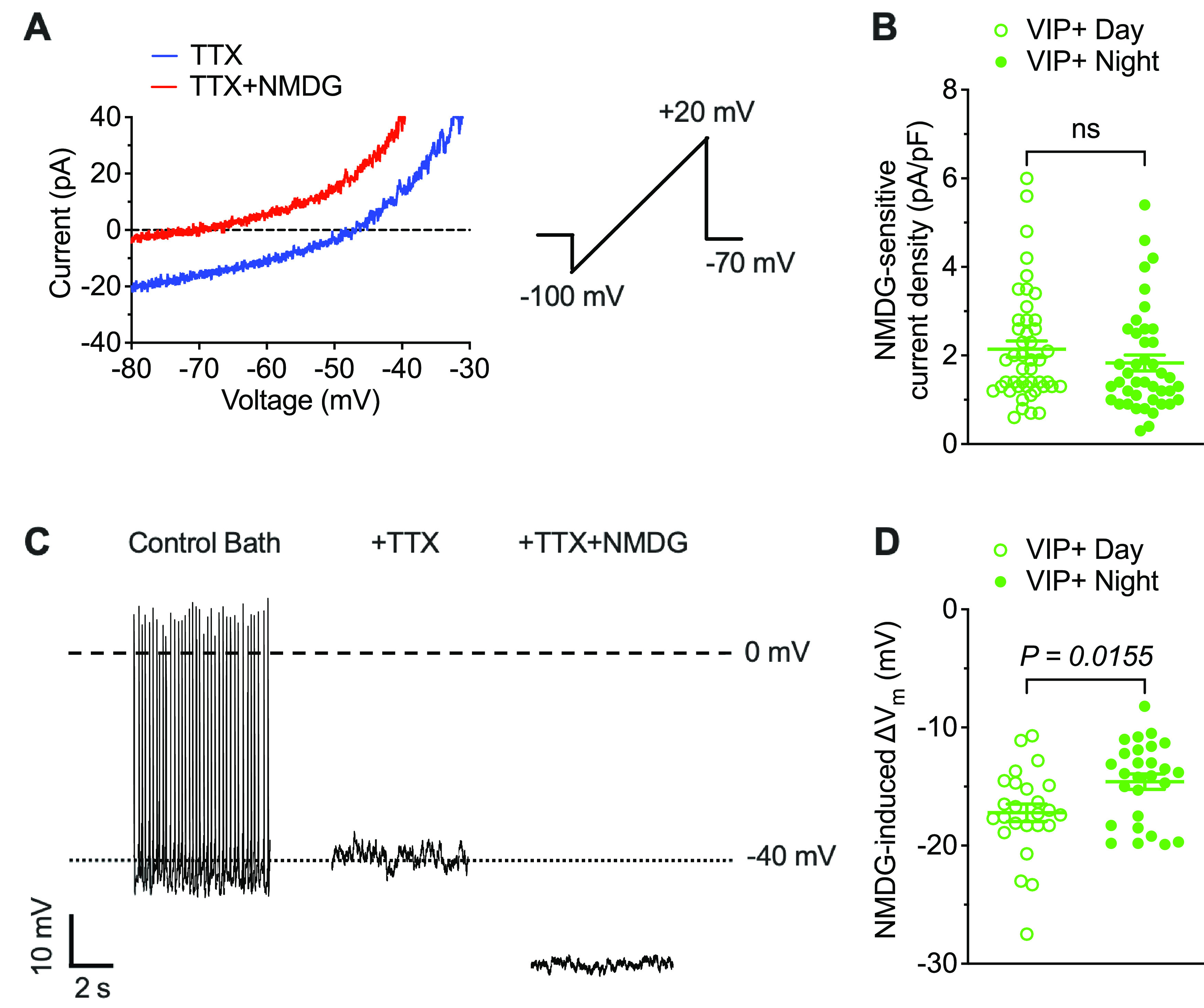
Differential effects of Na+ leak currents on the membrane potentials of daytime and nighttime VIP+ SCN neurons. A, Representative whole-cell currents recorded from a daytime VIP+ SCN neuron during slow voltage ramps (20 mV/s) in the presence of 1 μm TTX (blue) and following NMDG+ replacement of extracellular Na+ (red). Addition of NMDG+ decreases inward current amplitude. B, NMDG-sensitive Na+ leak current densities measured in daytime (open circles, n = 46) and nighttime (filled circles, n = 42). VIP+ SCN neurons are not significantly different. C, Representative whole-cell current-clamp recording from a daytime VIP+ SCN neuron showing spontaneous action potential firing in control bath solution. The addition of 1 μm TTX eliminates firing but does not affect the resting membrane potential. The subsequent replacement of extracellular Na+ with NMDG+, however, hyperpolarizes the membrane potential. D, NMDG-induced changes in the membrane potentials of VIP+ SCN neurons during the day (open circles, n = 25) and at night (filled circles, n = 27) are shown. Data are mean ± SEM; p values are also indicated. See Extended Data Figure 2-1 and Extended Data Table 2-1.
