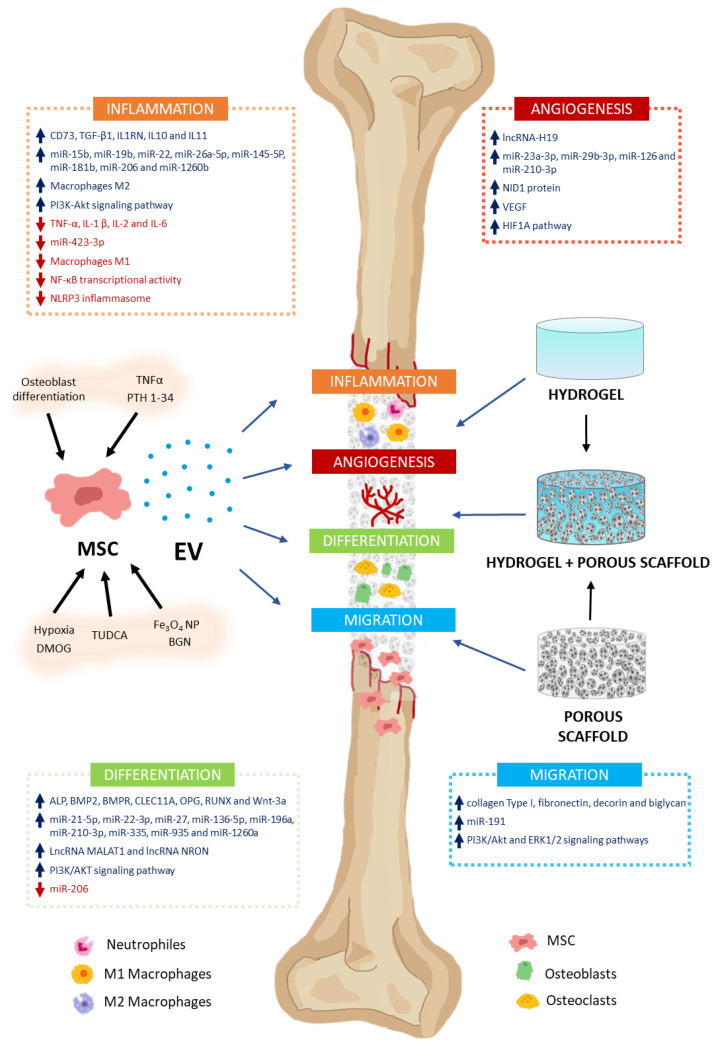
Figure 2.
Effects of MSC-EV on bone regeneration. MSC-EV have the capacity to modulate different processes related to bone formation and regeneration. They include inflammation, angiogenesis, differentiation, and cell migration. This is due to their cargos, which have high (↑) or low (↓) levels of different molecules with biological activity (growth factors, cytokines, miRNA, lncRNA, etc.). They intervene in the induction or inhibition of different signaling pathways related to these processes. To stimulate secretion of EV with high regenerative capacity in MSC cultures, cells can be preconditioned with different molecules [TNFα, PTH 1-34, tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), and dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG)], nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NP), bioactive glass nanoparticles (BGN), or culture conditions (osteoblast differentiation and hypoxia). MSC-EV can be applied for the treatment of bone defects, incorporating them into biomaterials that serve as vehicles and delivery systems for them. Thus, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation are facilitated in the scaffolds, enabling bone regeneration. Hydrogels, porous scaffolds, and those resulting from the combination of both are interesting biomaterials with great potential for treating bone damage.