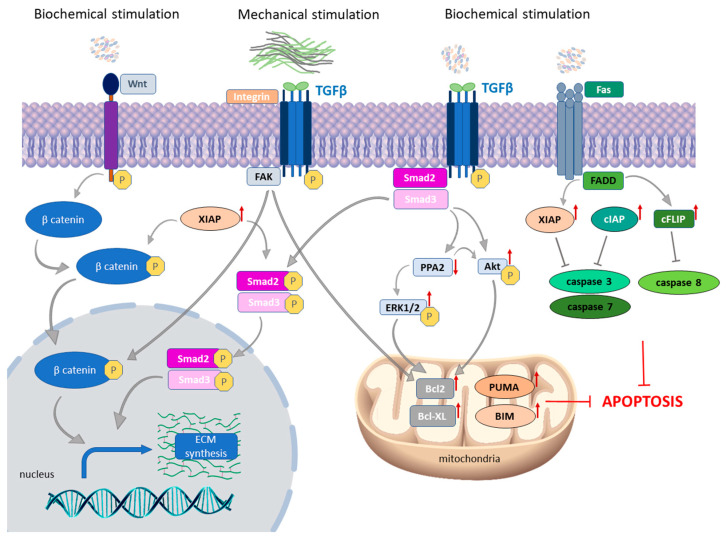
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of apoptosis regulation in SSc. In the skin of SSc patients, both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways are deregulated. In response to biochemical stimulation, both canonical and non-canonical TGF-β pathways are activated, and XIAP is shown to be a link between them. XIAP also inhibits caspase-3 and 7. As a result of constitutively activated autocrine TGFβ signaling, PP2A level is downregulated in SSc fibroblasts, leading to increased AKT and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Extrinsic apoptotic pathway is deregulated through cIAP and XIAP proteins. Their higher expression was shown to abrogate caspase-3 and 7 in late-stage fibroblast populations from SSc patients. Matrix stiffness through the activity of fibroblast integrins transmits the mechanical force from the matrix to the actin cytoskeleton through focal adhesion-associated protein FAK. FAK activation and its constitutive phosphorylation of downstream molecules drives profibrotic gene expression. In addition, target genes regulated through this mechanism also include proapoptotic BCL-2 family members Bcl-2, BIM, and PUMA, which activate to prime the cell for apoptosis. In response to this, extensive activation of antiapoptotic Bcl-XL protein takes place, in order to ensure cell survival.