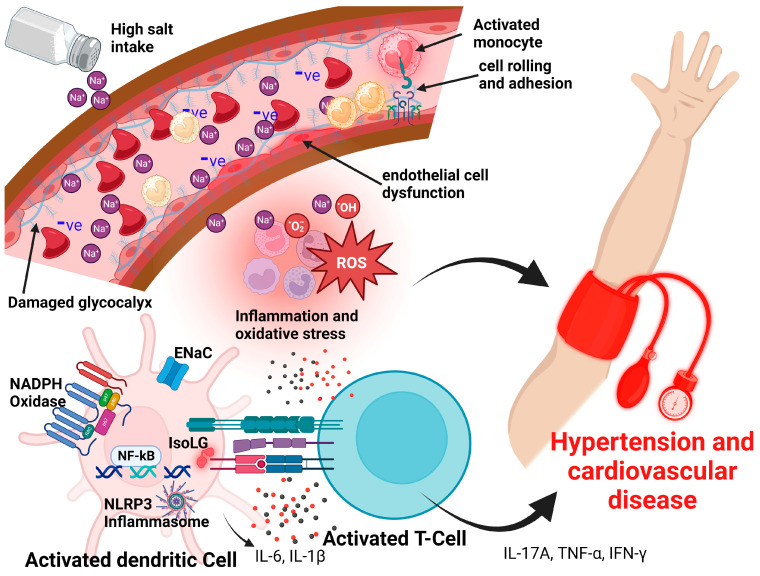
Figure 3.
Proposed model of salt-induced damage to the glycocalyx that results in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. High intake of salt damages the glycocalyx and induces inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune activation, thus leading to the development of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. ROS, reactive oxygen species; ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NLRP3, NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3; NF-Κb, Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IsoLGs, Islovuglandins; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IFN-γ, Interferon gamma.