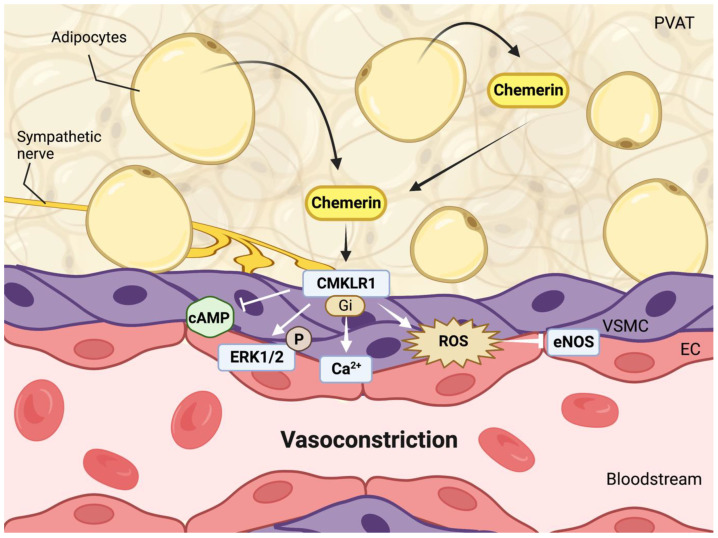
Figure 3.
Chemerin-induced vasoconstriction involves both direct effects via its type 1 receptor (CMKLR1) on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), mediated via cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) reduction, upregulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and indirect effects mediated via activation of the sympathetic nervous system. NO, generated by endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) in endothelial cells (EC), will counteract the effects of chemerin. Data are from references [24,26,28,35,143].