Fig. 4 |. Immunosurveillance by CD4+ T cells.
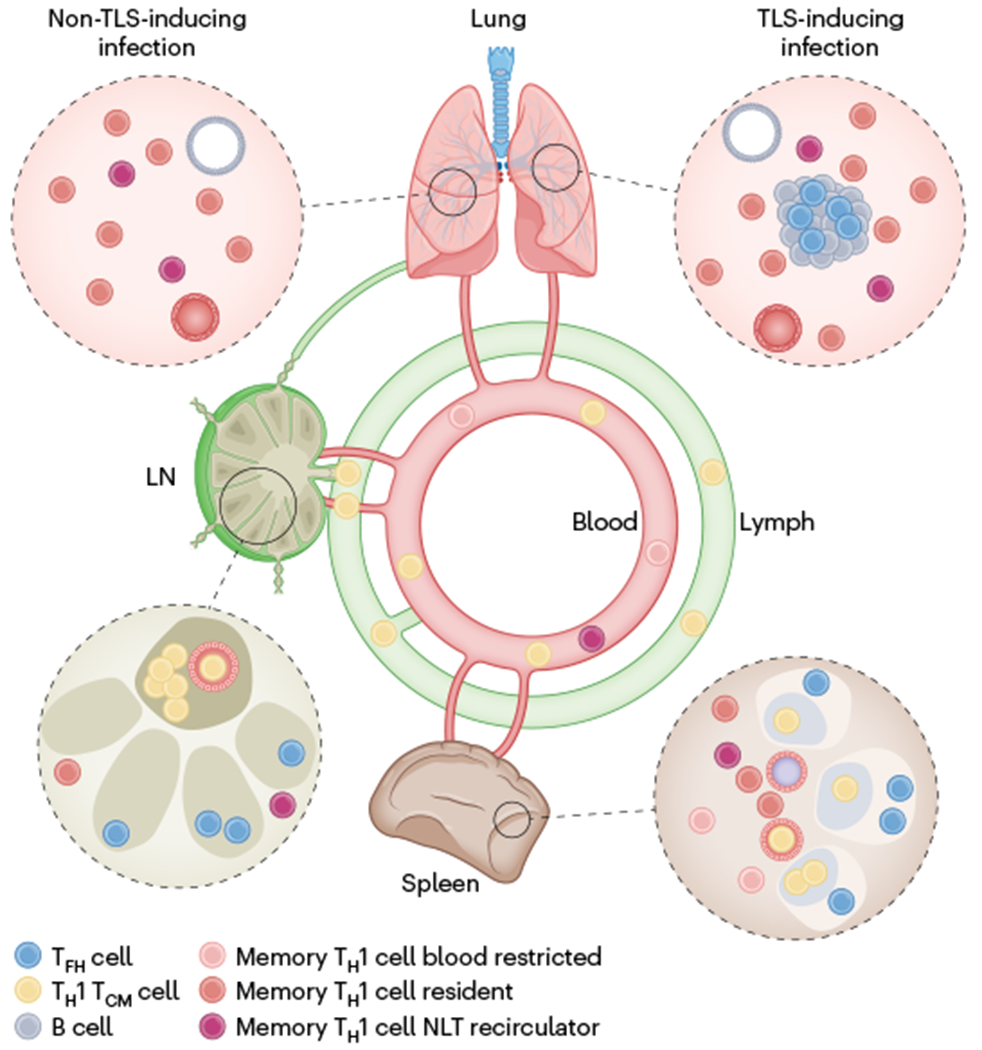
Memory CD4+ T cell immunosurveillance strategy after a respiratory viral infection that elicits a type I response. Although we focus on memory TH1 cells, both memory TH2 and memory TH17 cells have been well documented to take up permanent residence in NLTs. In contrast to TH1 TCM cells, which express CD62L, many memory TH1 cells cannot access lymph nodes (LN) through high endothelial venules. These memory TH1 cells in lymph nodes might represent TH1 cells that recirculate constitutively through NLTs and enter lymph nodes through afferent lymphatics (‘backdoor entry’) from upstream NLTs, or SLO-resident memory TH1 cells. Memory TH1 cells in the blood comprise blood restricted cells, NLT recirculators and TCM cells. FR4hi memory TFH cells populate SLOs and may reside at the outer boundaries of B cell follicles. TFH-like CD4+ TRM cells have been identified in lungs of influenza-infected mice. In contrast to resident TH1 cells, resident TFH cells seem locally restricted to TLSs.
