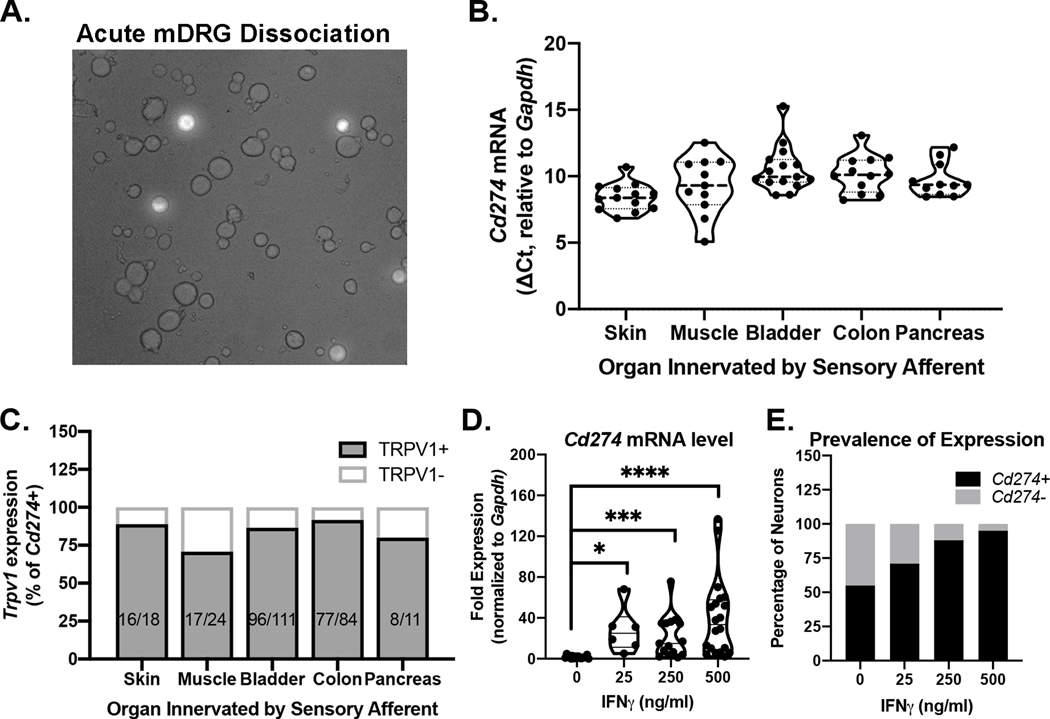
Figure 2. Cd274 and Pdcd1 mRNA expression in individual spinal sensory neurons.
mRNA analyses were conducted on individual retrogradely labeled sensory neurons collected following dissociation of DRG that innervate the targeted tissue (Panel A-C) or from dissociation of all DRG (Panel D,E). (A) Representative image of acutely dissociated mouse DRG revealing fluorescent labeling of colon afferents (20X). (B) Cd274 mRNA, but not Pdcd1 mRNA was detected in individual neurons innervating skin, muscle and visceral organs including colon, bladder, and pancreas. (C) Trpv1 mRNA was detected in 70.8–91.7% of neurons in which Cd274 mRNA was also detected. (D) DRG neurons incubated with IFNγ overnight show significantly increased levels Cd274 mRNA expression. Fold expression was calculated using the ΔΔCt method. Neurons were collected from two independent experiments (Kruskal-Wallis Test followed by Dunn’s post-hoc test, H=32.75, df=4, p<0.001). (E) IFNγ increases the proportion of neurons expressing detectable levels of Cd274 mRNA. Data are pooled from two independent experiments (chi-square test X2(3, n=33)=12.07, p=0.007).