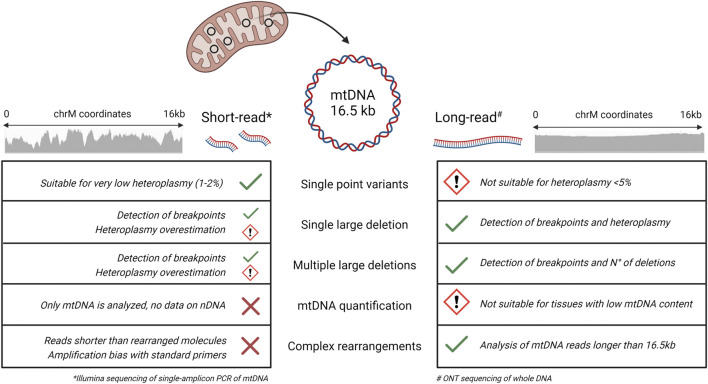
FIGURE 5.
Short and long-read performance comparison for the sequencing of mtDNA. Summary of the performances of short-read (Illumina) and long-read (ONT) sequencing in the detection of different mtDNA alterations. For evaluation of short-reads, we used the single amplicon protocol described by (Legati et al., 2021), while for long reads we referred to the present study. Short-read NGS is suitable for identifying single point variants, even at very low heteroplasmic percentages, but the use of reads of 150–300 bp in length hampers the detection of large deletions and complex rearrangements. Long-read NGS shows multiple advantages in the analysis of mtDNA alterations, with some limitations regarding the minimum heteroplasmy detectable for single point variants and the quantification of mtDNA in tissues characterized by a lower content of mitochondria. (Image created with BioRender.com).