FIGURE 4.
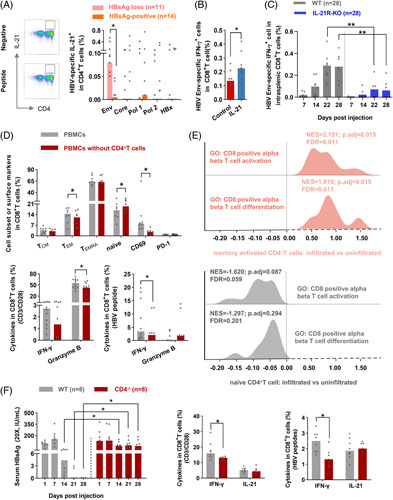
CD4+ T cells favor CD8+ T-cell–mediated cellular immune responses. Representative FACS plots showed the staining of IL-21-producing HBV-specific CD4+ T cells. The frequency of IL-21-producing HBV-specific CD4+ T cells in HBsAg loss and HBsAg-positive patients with 96 weeks of therapy discontinuation. (B) The frequency of IFN-γ-producing HBV Env-specific CD8+ T cells from patients with chronic HBV infection after stimulated with recombination human IL-21 (IL-21) and PBS (control), respectively (n=8) for 10 days. (C) WT and IL-21R-KO mice were injected with pAAV-HBV1.2 HDI. Splenic lymphocytes were stimulated with HBV Env peptide pools for 6 hours; the frequency of IFN-γ-producing HBV-specific intrasplenic CD8+ T cells was detected at indicated time points. (D) Bulk PBMCs and corresponding PBMCs with CD4+ T-cell depletion from patients with therapy withdrawal (n=12) were cultured without a stimulant for 5 days, or stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 3 days, or stimulated with HBV peptides for 10 days. The cell subset, CD69, PD-1, granzyme B, and IFN-γ expression on CD8+ T cells in bulk PBMCs and PBMCs without CD4+ T cells were compared. (E) The data analysis from NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus (GSE83148) included 122 CHB patients. Hepatic infiltrated immune cells (memory-activated CD4+ T cells and naïve CD4+ T cells) and uninfiltrated immune cells were compared in liver tissues using the CIBERSORT web portal. GSEA was conducted to evaluate the effect of memory-activated CD4+ T cells (pink, upper panel) and naïve CD4+ T cells (gray, lower panel) on CD8+ T-cell activation and differentiation gene ontology pathway. (F) WT and CD4-/- mice were injected with pAAV-HBV1.2 HDI. Concentrations of HBsAg (20×, IU/mL) were measured. The frequency of total and HBV-specific IFN-γ+CD8+ and IL-21+CD8+ T cells were detected in WT and CD4-/- mice. (A–D, and F) Mann–Whitney U test or paired Wilcoxon test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Abbreviations: Env, Envelope; GO, gene ontology; GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis; HDI, hydrodynamic injection; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; Pol, Polymerase; TCM, central memory T; TEM, effector memory T; WT, wild type.
