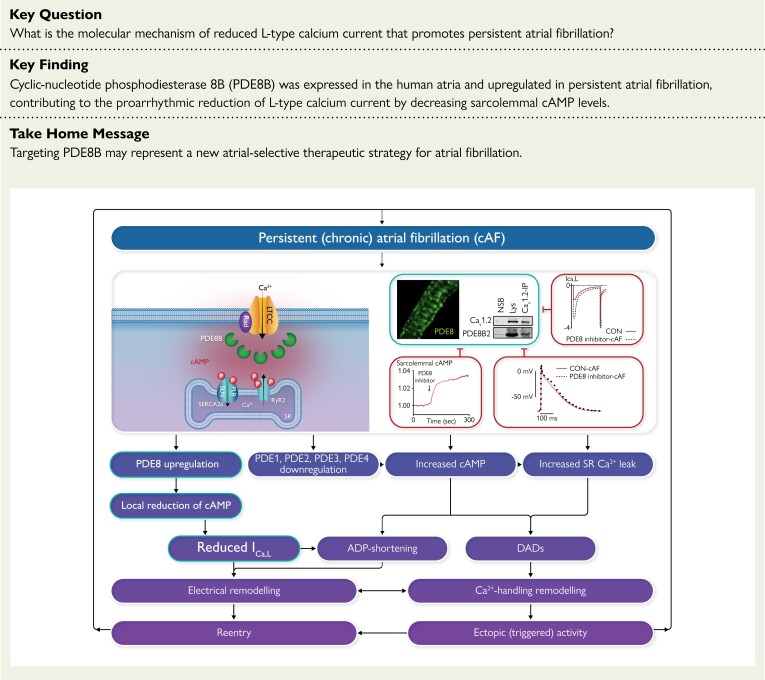
Structured Graphical Abstract.
The reduction of L-type Ca2+-current in atrial myocytes promotes atrial fibrillation. Phosphodiesterase type 8B binds L-type Ca2+ channels and reduces local cAMP levels and PKA-dependent channel phosphorylation, thereby decreasing L-type Ca2+-current and abbreviating atrial action potential that promotes atrial fibrillation persistence. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; cAF, persistent (chronic) atrial fibrillation; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DAD, delayed afterdepolarization; ICa,L, L-type Ca2+ current; LTCC, L-type Ca2+ channel; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PLB, phospholamban; RyR2, ryanodine receptor type 2; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2 + ATPase type 2a; SLN, sarcolipin; SR, sinus rhythm.