Fig. 1.
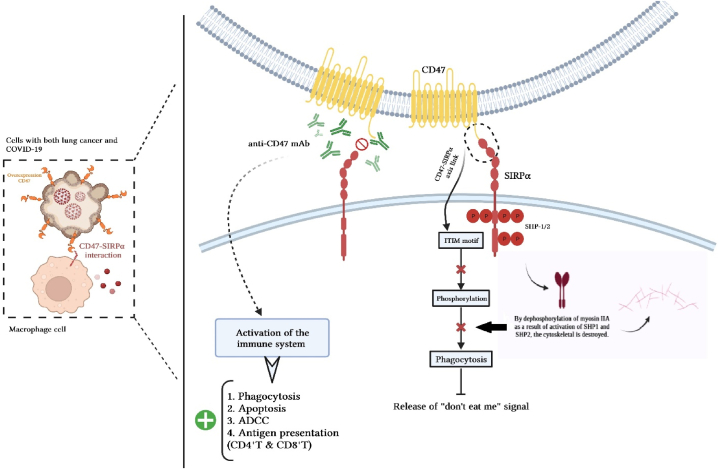
CD47, the link between cancer & COVID-19. The engagement of CD47-SIRPα plays an essential role in inhibiting the phagocytosis process. The interaction of CD47-SIRPα with phosphorylation of SHP1/2 in the ITIM motif triggers a series of events in the form of a signaling cascade to cause dephosphorylation of myosin IIA, which is an important stage in the phagocytic activity of macrophages. CD47-SIRPα interaction is associated with increased CD47 expression in tumor or SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Immunotherapy by innate immune cells, including macrophages, is a new therapeutic perspective in understanding the common molecular pathways of cancer and COVID-19. It directly inhibits non-self-cells and promotes immunotherapy via T cells. The use of anti-CD47 mAb to blockade CD47-SIRPα is a potential therapeutic strategy in the deadly duo of COVID-19 and cancer. Early detection of other signaling pathways such as anti-MHC1 (or antiLILRB1) will regulate phagocytosis by macrophages.