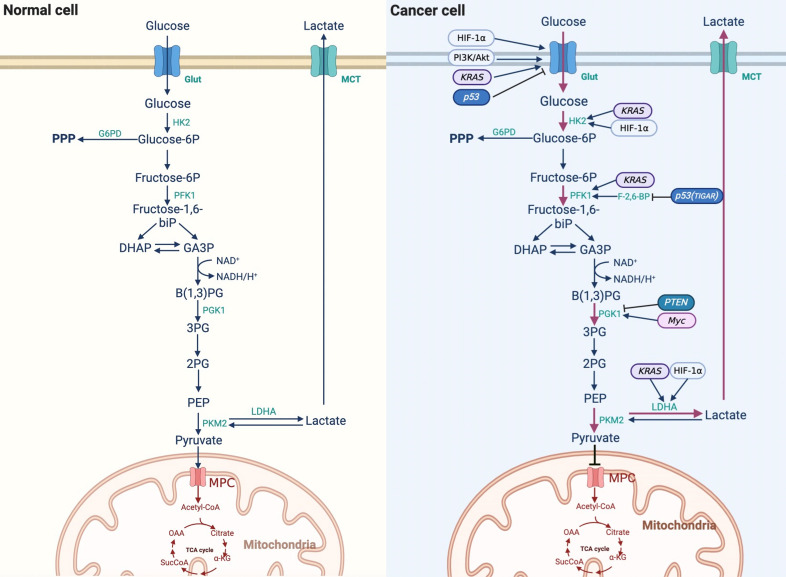
Figure 1.
Difference of reprogramming of glucose metabolism between normal cells and cancer cells. 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; Akt: protein kinase B; B(1,3)PG: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate; F-2,6-BP: fructose-2,6-diphosphate; GA3P: glyceraldehyde3-phosphate; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HK2: hexokinase 2; KRAS: kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene; MCT: monocarboxylic acid transporter; MPC: mitochondria pyruvate carrier; NAD+: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidation state); NADH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reducing state); OAA: oxaloacetic acid; PFK1: phosphofructokinase 1; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PGK1: phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKM2: M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; SucCoA: succinyl-coenzyme A; TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle