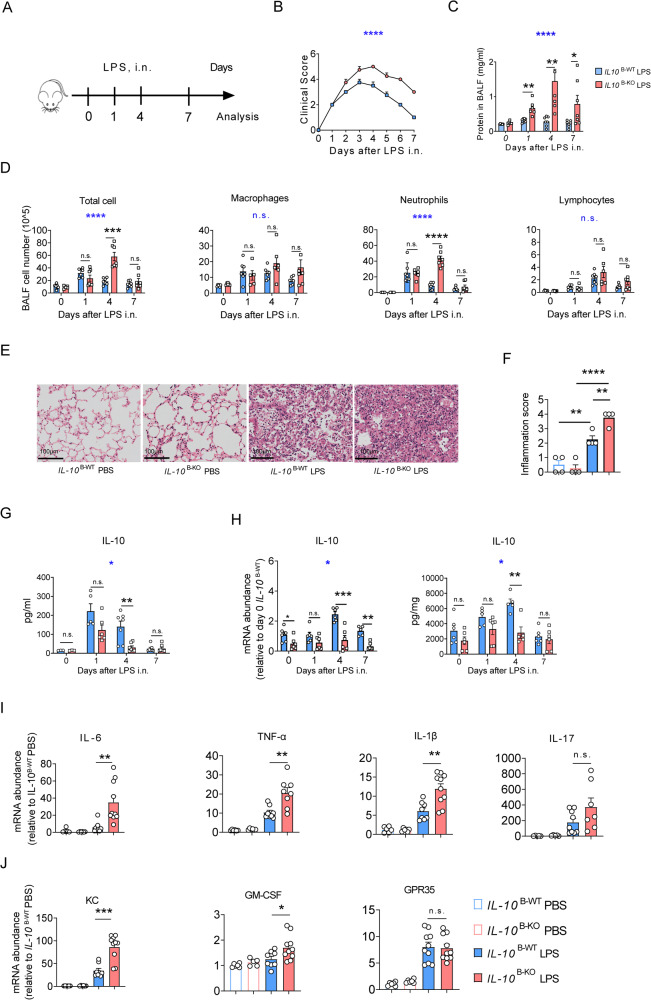
Fig. 4. Interleukin (IL)-10 in B cells promotes acute lung injury (ALI) recovery.
A Experimental scheme: Observation and analysis of recovery from acute lung injury in IL-10 B-WT and IL-10 B-KO mice at days 1, 4, and 7 after LPS exposure. B Clinical signs in mice were observed (n = 6–7). C Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from IL-10 B-WT and IL-10 B-KO mice was harvested, and the protein concentration was measured (n = 4–7). D IL-10 B-WT and IL-10 B-KO mice were treated with 50 μg LPS i.n., and BALF of the treated and control mice were harvested on days 1, 4, and 7. The total BALF number of cells and different types of cells were counted (n = 6–7). E, F The representative image of the HE-stained section and the inflammation score are displayed (n = 4). Scale bars, 100 μm. G IL-10 protein levels in BALF. H IL-10 mRNA and protein levels in the lung. I mRNAs of IL-6, TNF-α, IL1-β, and IL-17, were detected in lung homogenates (n = 6–8). J mRNAs of KC, GM-CSF, and GPR-35 were detected in lung homogenates (n = 6–8). B–D, G, H Two-way ANOVA was used for the statistical analyses (blue stars). (C, D, F–J) Student’s t-test was used for the two groups’ statistical analyses (black stars).