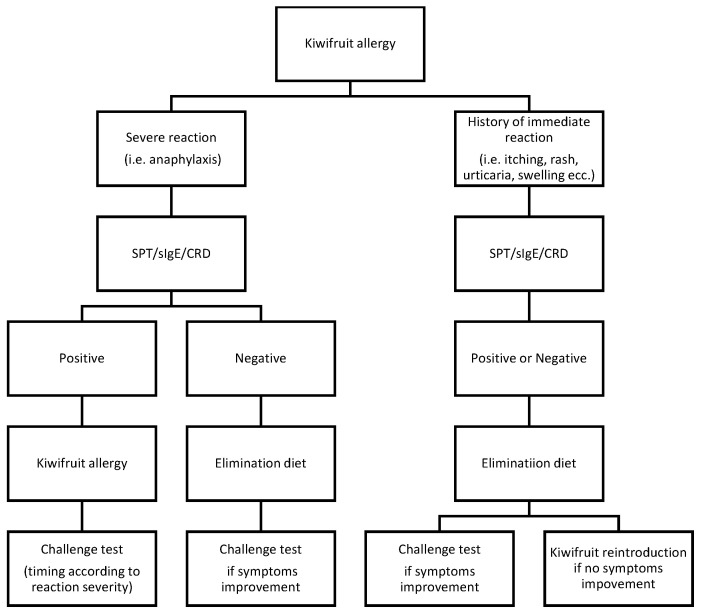
Figure 1.
Diagnostic flowchart. Patient personal histories of severe reactions need to be tested via SPT, RAST, and CRD. Anaphylaxis is indicated by “severe reaction”. In this case, if the laboratory test result is positive, a food allergy is claimed; the timing for the challenge test is decided after considering the clinical response and the outcome of the CRD test. If the serological exams are negative, a focused elimination diet should follow. Based on the diet change response, the challenge test becomes worthy in revealing the diagnosis. The diagnostic process is similar in patients with immediate nonsevere reactions after kiwifruit ingestion, such as rash, urticaria, dyspnea, intense coughing, swelling of tongue, lips, and extremities, and itching. Apart from the results of the diagnostic tools, an elimination diet should be implemented. If relief from symptoms is achieved, the challenge test should be performed; on the contrary, it is possible to reintroduce the food, especially with negative serum diagnostic test results (including the CRD) [40]. In this case, there is no evidence to claim the specific kiwifruit allergy.