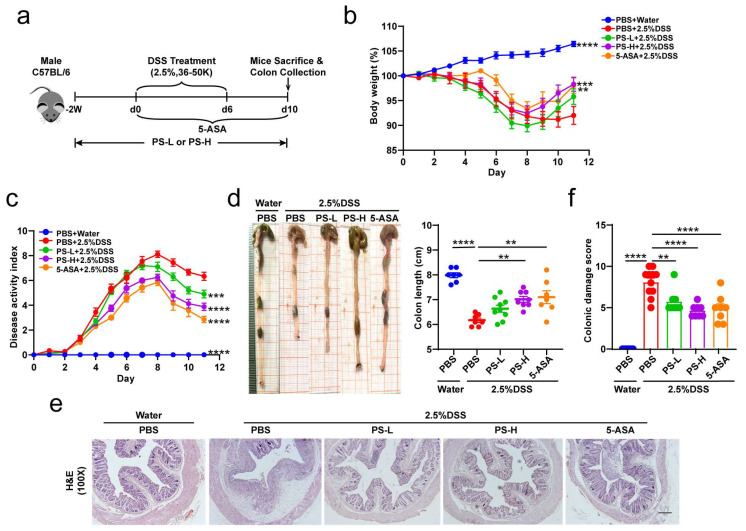
Figure 1.
Oral PS attenuates DSS-induced colitis. (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the experimental system: C57BL/6 mice received a daily oral gavage of normal saline or low dose of PS (PS-L) or high dose of PS (PS-H) starting 2 weeks before being subjected to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis and sustained until the end of the experiment. Mice were treated with 2.5% DSS in drinking water ad libitum for 6 days; 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) was served as a positive control and was administered on the day that DSS treatment started. n = 16 mice per group. (b) Daily mean body weight changes in each group described in (a). n = 7–10 mice per group. (c) Changes in DAI score (composited score of body weight, bleeding, and stool consistency) after water or DSS oral treatment. n = 7–10 mice per group. (d) Representative colons from each group described in (a) and statistical analyses for colon length. n = 7–9 mice per group. Representative photomicrographs (100×) of colon tissue staining by H&E ((e), scale bar = 200 μm) and quantitative analyses for colonic damage scores ((f), n = 7–9 mice per group). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 as determined by one-way ANOVA (b–e). Data represent mean ± SEM.