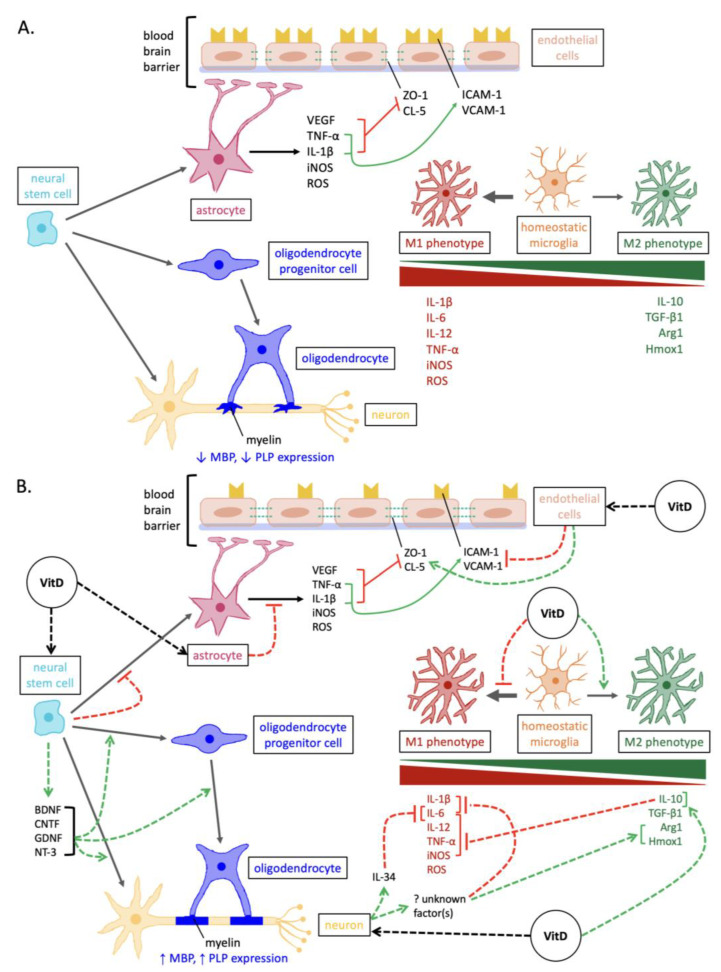
Figure 1.
Overview of the mechanisms involved in neurodegeneration versus vitamin D-mediated neuroprotection in MS. (A) Pathways of neurodegenerative pathogenesis in MS. In addition to the depicted, the expression of neurotrophins and antioxidant enzymes is reduced in neurons and glia. (B) Neuroprotective pathways elicited by vitamin D in MS. Abbreviations: Arg1, arginase 1; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CNTF, ciliary neurotrophic factor; CL-5, claudin-5; GDNF, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; Hmox1, heme oxygenase 1; ICAM-1, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL, interleukins; MBP, myelin basic protein; NT-3, neurotrophin-3; PLP, proteolipid protein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ZO-1, zonula occluden-1.