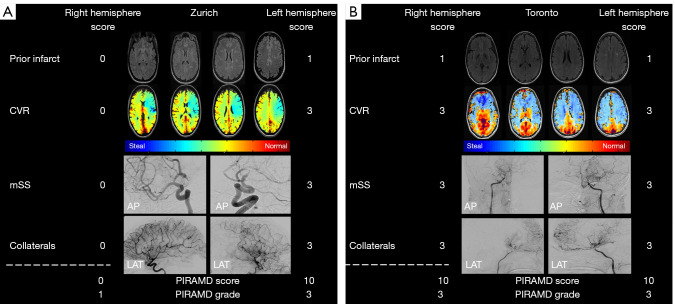
Figure 3.
Illustration of PIRAMD scoring system for an individual patient from both centers. (A) An exemplary patient from the Zurich database where the PIRAMD scoring system is applied (i.e., prior infarct determination on T2-weigthed FLAIR MRI, determination of impaired cerebrovascular reactivity from BOLD fMRI CVR imaging, determining a modified Suzuki Grade Score, and assessment of the number of impaired collaterals on DSA using the modified APECTS score). With the presence of an prior infarction in the left hemisphere (1 point), the presence of negative (blue) BOLD-CVR in the anterior circulation (3 points) and the presence of an mSS >2 and the presence of impaired collateralization (both 3 patients), the patient obtained 10 points for his left hemisphere, while the contralateral hemisphere displayed none of these characteristics (0 points). (B) The determination of the PIRAMD Score for an individual patient from the Toronto database. These patients with Moyamoya disease displayed a bilateral disease and were classified with 10 patients for both hemispheres. CVR, cerebrovascular reactivity; mSS, modified Suzuki Score; AP, anterior-posterior; LAT, lateral; PIRAMD, Prior Infarcts, Reactivity, and Angiography in Moyamoya Disease; FLAIR, fluid attenuated inversion recovery; BOLD, blood-oxygenation-level dependent; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; DSA, digital subtraction angiography.