Figure 2. Azetidine acrylamides stereo- and site-selectively engage recombinant DCAF1_C1113.
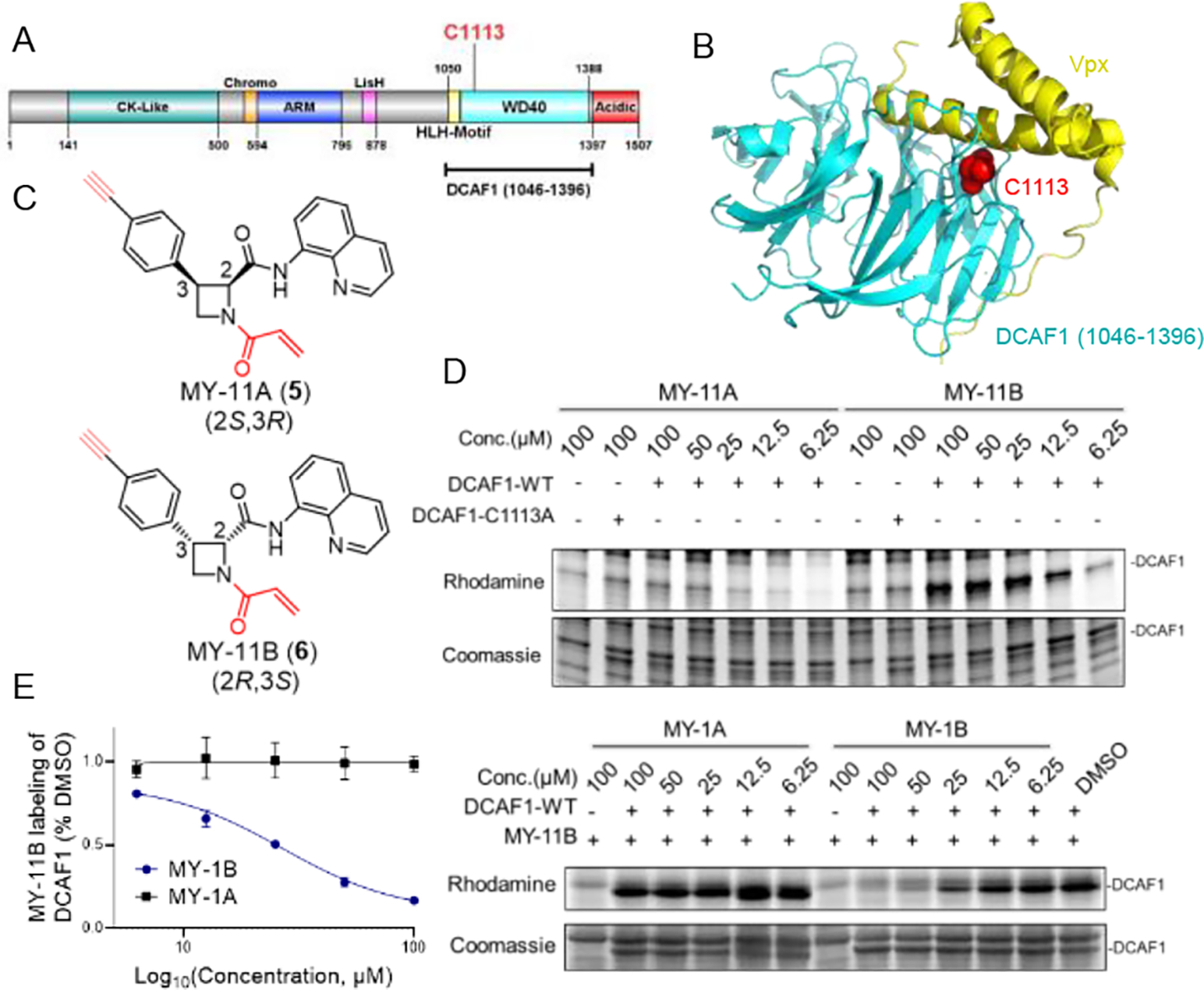
(A) Domain map of DCAF1 with the region used for recombinant protein studies marked in a bracket (aa 1046–1396) and C1113 highlighted in red. (B) Crystal structure of a DCAF1-Vpx complex (pdb: 5AJA). DCAF1 (aa 1046–1396) is shown in cyan, Vpx is shown in yellow, and C1113, which is located at the DCAF1-Vpx interface is shown in red. (C) Structures of alkyne-modified azetidine acrylamides MY-11A (5) and MY-11B (6). (D) Gel-ABPP showing the concentration-dependent reactivity of MY-11A and MY-11B (1 h) reactivity with recombinant, purified DCAF1-WT or the DCAF1-C1113A mutant (0.06 μg/μL of DCAF1 protein per sample) doped into HEK293T cell proteome (1 μg/μL). MY-11A/B labeling of proteins was visualized by CuAAC conjugation to an azide-rhodamine tag followed by SDS-PAGE and in-gel fluorescence scanning. Results are from a single experiment representative of two independent experiments. (E) Gel-ABPP showing the concentration-dependent effects of MY-1A and MY-1B on MY-11B reactivity with DCAF1-WT. Samples were treated with MY-1A/B for 2 h, followed by MY-11B (25 μM, 1 h) and analyzed as described in (D). Left, quantification of data presented as mean values ± SEM from two independent experiments. Right, representative gel-ABPP results. (D, E) Lower images are Coomassie blue-stained gels corresponding to ABPP gels shown in upper images.
