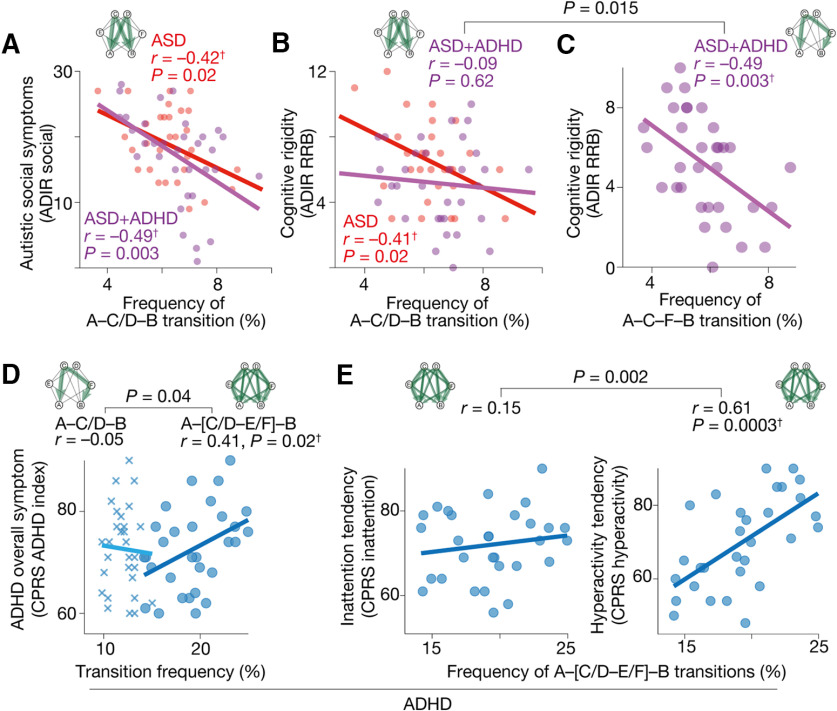
Figure 3.
Brain state dynamics and symptoms. Three brain-state transitions exhibited symptom-specific atypical frequencies. A, In both the pure ASD and ASD+ADHD groups, the severity of the autistic socio-communicational symptom (ADI-R social) was negatively correlated with the A–C/D–B transition frequency. B, This A–C/D–B transition frequency explained the cognitive rigidity (ADI-R RRB) of the pure ASD children but did not that of the ASD+ADHD individuals. C, Instead, the cognitive rigidity of the ASD+ADHD children was correlated with their atypically frequent A–C–F–B transition. D, The ADHD symptom in the pure ADHD children was not explained by this A–C–F–B transition frequency but by the A–[C/D–E/F]–B transition frequency. E, In particular, the atypical increase in the A–[C/D–E/F]–B transition frequency was specifically correlated with the hyperactivity tendency in the pure ADHD group. †pBonferroni < 0.05.