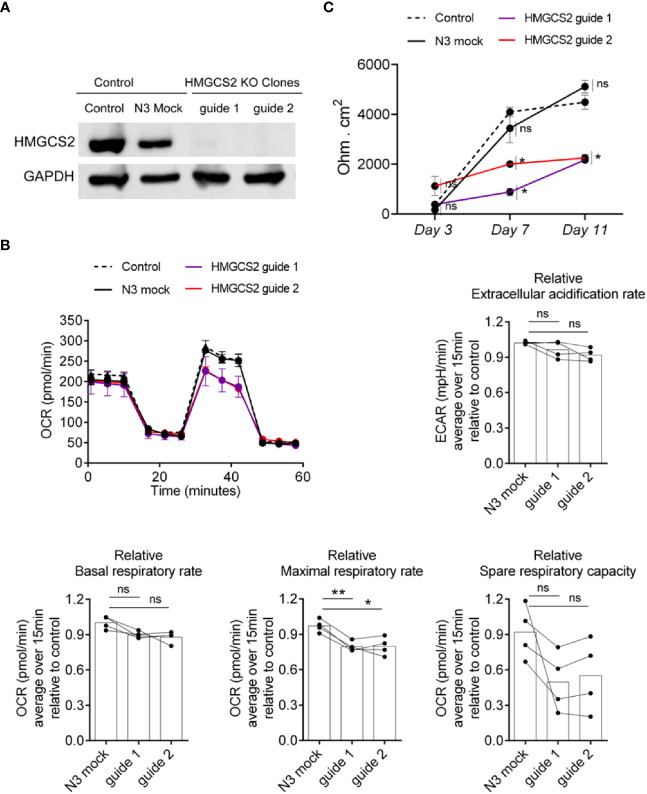
Figure 7.
HMGCS2 absence associates with functional alterations in Caco-2 cells. (A) CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of HMGCS2. Immunoblot showing HMGCS2 protein expression in parental cells (Control), Mock cells (N3) and two different clones of HMGCS2 knock-out cells (guide 1 and guide 2 respectively), normalized to GAPDH expression. (B) HMGCS2 knock-out cell lines have a deficient Maximal Respiratory Rate. Bioenergetic analyses of Control Caco-2 (control parental cells and Mock Caco-2) and HMGCS2-deficient Caco-2 cell lines in medium with 5mM butyrate in response to different metabolic inhibitors. The results are normalized to control parental Caco-2 cell values. Oxigen consumption rates (OCR) and Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) were measured three times over 15 minutes as a readout for the mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis respectively. Data shows a representative respiration plot (up left) or the mean and paired individual data points of 4 independent experiments. One-Way ANOVA corrected with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used. ns not significant (P>0.05), *P<0.05 **P<0.01. (C) Knockout of HMGCS2 increases the permeability of the intestinal monolayer. Control Caco-2 (control parental cells and Mock Caco-2) and HMGCS2-deficient Caco-2 cell lines at steady-state (basal) were seeded at the same concentration using complete DMEM medium. TEER was measured at the indicated time points and is given as raw TEER measurements normalized to wells without cells. Data represents the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA corrected with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used. ns not significant (P>0.05), *P<0.05.