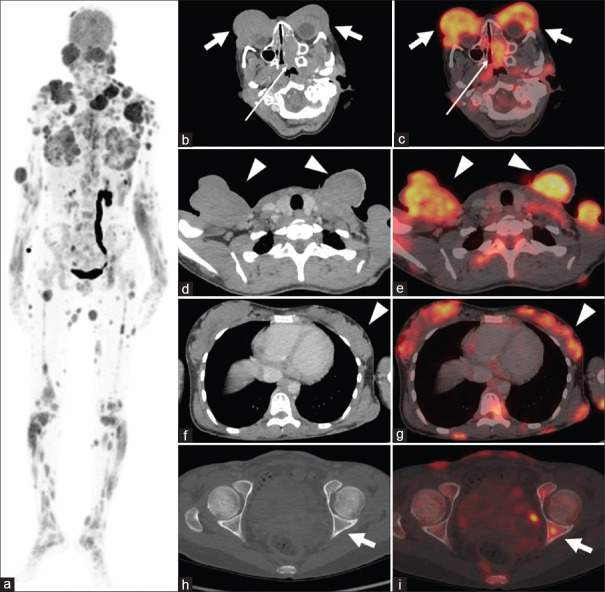
Figure 1.
(a) MIP (a) image showing multiple FDG-avid lesions throughout the whole body. Physiological FDG uptake is noted in the brain, kidneys, dilated left ureter, and bladder. (b-i) Axial CT and fused PET/CT showing intensely FDG-avid bilateral orbital swellings (b and c, thick white arrows), left nasal cavity lesion (b and c, thin white arrows), bilateral cervical and supraclavicular polypoidal lesions (d and e, white arrow heads), bilateral breast parenchymal nodular swellings (f and g, white arrow heads), and bone marrow deposits (h and i, thick white arrows). MIP: Maximum intensity projection, FDG: Fluoro-2-deoxyglucose, PET CT: Positron emission tomography and computed tomography