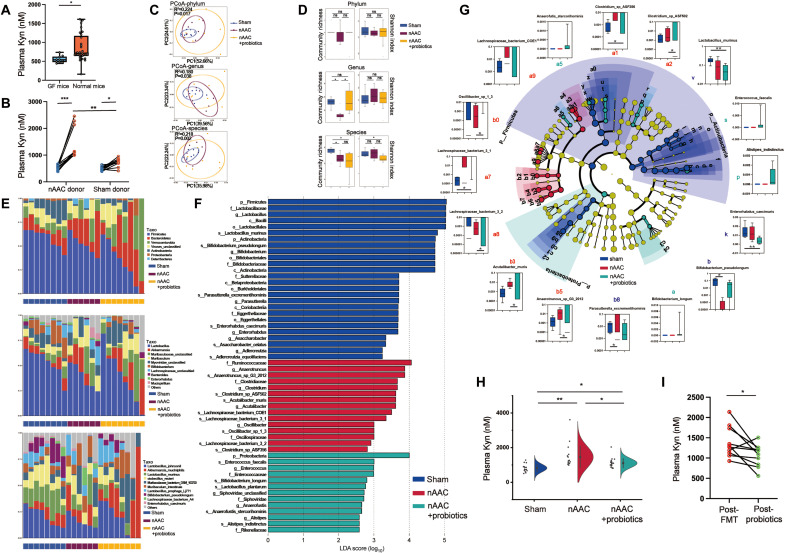
Fig. 6. Probiotics reconstructs gut microbiota of nAAC mice and reduces plasma Kyn.
(A) UHPC-MS/MS quantification of baseline Kyn concentration between the GF mice (n = 10) and C57BL/6 mice (n = 39). (B) UHPC-MS/MS quantification of plasma Kyn concentration in GF mice before (pre-FMT) and after (post-FMT) 2 weeks of FMT from nAAC or sham donor mice (n = 10). (C) PCoA by Bray-Curtis distance at phylum (R2 = 0.224, P = 0.017), genus (R2 = 0.180, P = 0.038), and species level (R2 = 0.218, P = 0.002) in metagenomics sequencing among the feces of sham (n = 8), nAAC (n = 6), and nAAC mice with probiotics (n = 8). Permutational multivariate ANOVA test was used. (D) Community richness and homogeneity (Shannon index) at genus, phylum, and species level among the three groups. (E) The relative abundance of top 10 microbes at phylum (top), genus (middle), and species (bottom). (F) Linear discriminate analysis effect size (LEfSe) to illustrate the specific microbes with top abundance that characterized each group. (G) Cladogram of the characterized microbes in each group, showing their evolutional and familial relationship (middle). Kruskal-Wallis rank sum tests (outer circle) were also conducted to demonstrate differential abundance of the specific microbes. (H) UHPC-MS/MS quantification of plasma Kyn concentration among 4-week-old mice with sham (n = 15), nAAC surgery (n = 19), and nAAC and probiotics supplement (n = 20). (I) UHPC-MS/MS quantification of plasma Kyn between GF mice with 2 weeks of FMT from nAAC donor mice (post-FMT) and after another 2 weeks of probiotics gavage (post-probiotics), n = 10. Two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used in (A), (B), and (I). Kruskal-Wallis test and post hoc Dunn test were used in (G). One-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc analysis were used for (H). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.