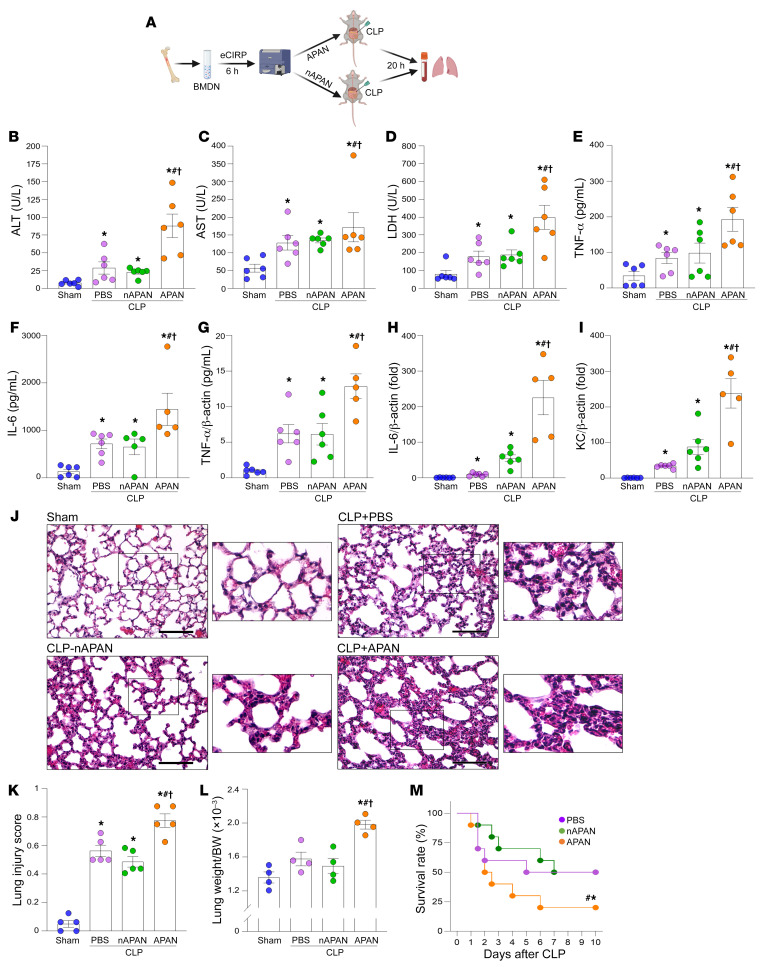
Figure 6. APANs exaggerate sepsis by fueling inflammation, lung injury, and worsening survival.
(A) BMDNs isolated from WT mice were stimulated with eCIRP for 6 hours. FACS-isolated APANs and nAPANs (1 × 106) were then adoptively transferred into mice via retro-orbital injection at the time of CLP. (B–I) Twenty hours later, the serum levels of (B) ALT, (C) AST, and (D) LDH were determined using specific colorimetric enzymatic assays; serum (E) TNF-α and (F) IL-6 levels were assessed by ELISA; and lung mRNA levels of (G) TNF-α, (H) IL-6, and (I) KC were assessed by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5–6 mice/group) and compared by ANOVA and SNK method. *P < 0.05 vs. sham, #P < 0.05 vs. CLP+PBS-treated mice, †P < 0.05 vs. CLP+nAPAN-injected mice. (J) Representative images of H&E-stained lung tissue. Original magnification, ×400. Scale bar: 100 μm. Enlarged images of the boxed areas are shown to the right. (K) Lung injury score. Average of 5 fields/slide/mouse. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5 mice/group) and compared by ANOVA and SNK method. *P < 0.05 vs. sham, #P < 0.05 vs. CLP+PBS-treated mice, †P < 0.05 vs. CLP+nAPAN-injected mice. (L) Wet lung weight–to–body weight (BW) ratio 20 hours after CLP. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 mice/group) and compared by ANOVA and SNK method. *P < 0.05 vs. sham, #P < 0.05 vs. CLP+PBS-treated mice, †P < 0.05 vs. CLP+nAPAN-injected mice. (M) Kaplan-Meier 10-day survival curve generated from PBS-, APAN-, and nAPAN-treated CLP mice. n = 20 mice/group, *P < 0.05 vs. CLP+PBS, #P < 0.05 vs. CLP+nAPAN-injected mice determined by the log-rank test.