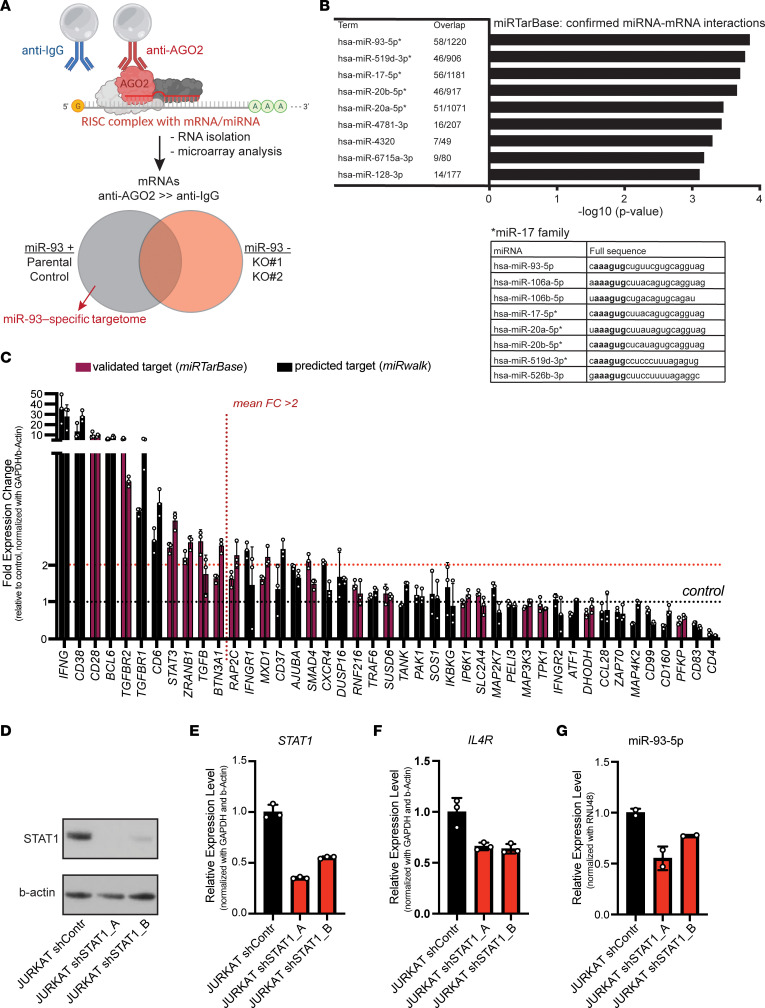
Figure 5. Identification of miR-93-5p target genes in sepsis and miR-93-5p upstream regulation.
(A) Schematic of the AGO2 IP method. Beads coupled to anti-AGO2 antibody or control (IgG) antibody are used to pull down the RISC complex including bound miRNA/mRNA interactors in the presence or absence of miR-93 expression. Putative miR-93 targets (n = 579) were defined as being enriched in the AGO2 IP of parental or control cells but not miR-93–KO cells. (B) Pathway analysis on 570 putative miR-93 target genes showed strong enrichment for previously known mRNA targets (miRTarBase) of miR-93 or other miR-17 family members that share the same seed sequence. The top 9 most enriched are shown. (C) Forty-three genes with immune functions that were identified in the AGO2 IP and validated (purple) or predicted (black) targets of miR-93-5p were assessed in JURKAT miR-93–KO cells compared with control by RT-qPCR. Bars indicate the mean fold change (FC) in gene expression in the KO 1 and KO 2 samples relative to control (control = 1). (D) STAT1 protein expression measured by Western blotting in cell lysates of JURKAT shControl, JURKAT shSTAT1_A, and shSTAT1_B cells. (E) STAT1 mRNA expression, (F) IL4 mRNA expression, and (G) miR-93-5p measured by RT-qPCR in JURKAT shControl, and JURKAT shSTAT1_A, and shSTAT1_B cells.