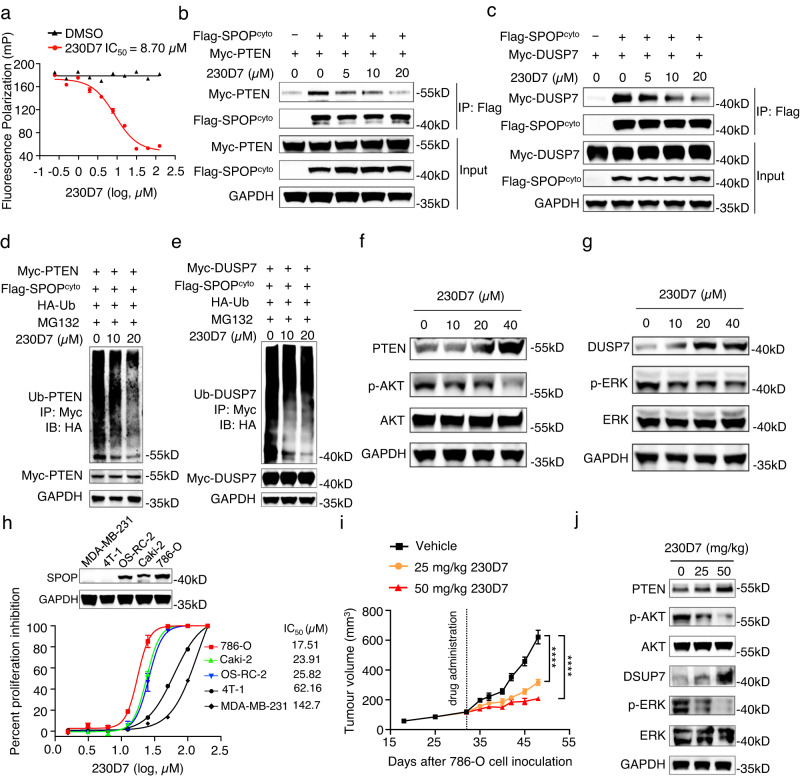
Fig. 5. 230D7 showed therapeutic potential for blocking oncogenic SPOP activity to treat ccRCC.
a 230D7 competitively inhibits puc_SBC1 peptide binding to SPOPMATH, as measured by the FP assay. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. b, c SPOP-PTEN and SPOP-DUSP7 protein interactions are inhibited in the presence of 230D7 in 293T cells. These experiments are repeated twice independently with similar results. d, e 230D7 inhibits the ubiquitination of PTEN and DUSP7 in 293T cells. These experiments are repeated twice independently with similar results. f, g 230D7 upregulates PTEN and DUSP7 protein levels in 786-O cells. The downstream p-AKT and p-ERK abundances are observed to decrease. These experiments are repeated twice independently with similar results. h Cell proliferations of three ccRCC cell lines and two non-ccRCC cell lines in the presence of 230D7. The abundance of cytoplasm SPOP protein was measured. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Western blot is repeated three times independently with similar results. i In vivo anti-ccRCC efficacy of 230D7 in 786-O xenograft models in NSG mice. Mice were administrated 230D7 at 25 or 50 mg/kg daily for 16 days by intraperitoneal dosing. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of seven biologically independent animals. P values were evaluated using 2-tailed unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001. (25 mg/kg 230D7 vs. Vehicle, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg 230D7 vs. Vehicle, P < 0.0001.) j Accumulation of PTEN and DUSP7 and repression of p-AKT and p-ERK at day 16 of 786-O xenograft tumors treated with vehicle or 230D7. This experiment is repeated twice independently with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.