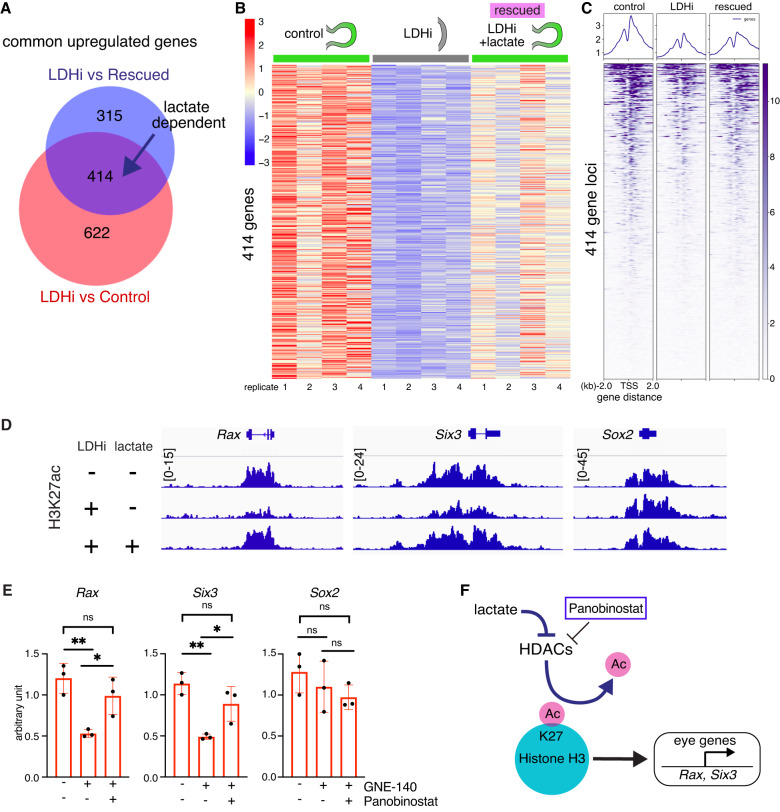
Fig. 6. HDAC and CBP/p300 activity specifically regulate eye developmental genes.
A Venn diagram reveals genes whose expression is dependent on lactate. B Heatmap of 414 lactate dependent differentially expressed genes. C Global histone H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac) chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIPseq) was performed in the following two conditions: 1) addition of the LDH inhibitor (20 µM), 2) addition of the LDH inhibitor in the presence of lactate (25 mM). The ChIP occupancy heatmaps showing H3K27ac plots at transcription start sites (TSS) (Enhancers/Promoters, +/−2 kb) of the differentially expressed genes identified from the RNA-seq analysis. D Bioinformatic analysis was performed and the ChIPseq data was visualized using the free software IGV (version 2.4.14) around coding and regulatory regions such as putative promoters and/or enhancers of some typical eye gene loci (Rax, Six3). Relatively higher peaks are seen in comparison with those upon adding the LDH inhibitor. This peak reduction when adding LDHi was recovered upon lactate treatment. E The pan-HDAC inhibitor Panobinostat was added to the organoids in the presence of LDHi from day 4 to day 5. Dual inhibition by LDHi and HDACi rescued eye marker genes at day 5, whereas pan-neural gene, Sox2 did not change dramatically as seen by qPCR. F Potential mechanisms regulating the eye developmental program through H3K27ac involving histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases. Panobinostat, a potent inhibitor depletes histone deacetylases (HDACs) mediated H3K27-deacetylation process. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test was performed (E). **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, n.s. nonsignificant (E). Data are presented as mean values +/−SEM (E). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. n = 3 biologically independent experiments were performed.