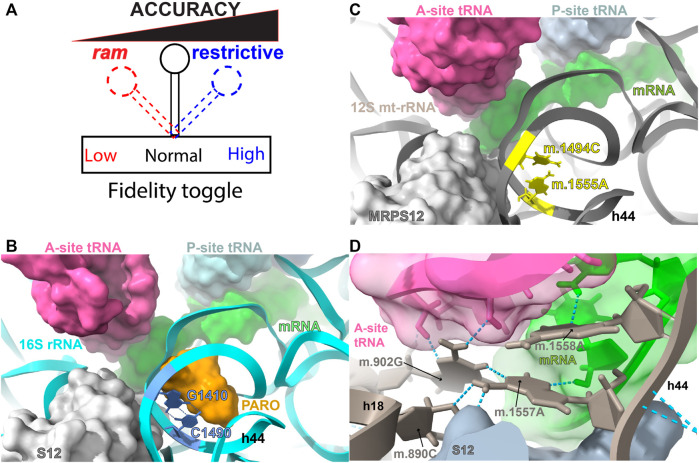
FIGURE 1.
DC and AG binding sites. (A) The ribosomal fidelity toggle. (B) Bacterial decoding center (DC) and aminoglycoside (AG) binding site. (C) Human mitochondrial DC and AG binding site. (D) Hydrogen bonding network during codon-anticodon recognition. The location of bacterial residues G1410 and C1490 (blue) of 16S rRNA (T. thermophilus) and 847C (m.1494C) and 908A (m.1555A) (yellow) of 12S mt-rRNA are shown in (B,C). Hydrogen bonds between G1410 and C1490 are indicated by blue, broken lines in (B). The aminoglycoside antibiotic paromomycin (orange), present in the bacterial structure, is shown in orange in B. Other important molecules present in the decoding center (A-, P-site tRNA, mRNA, and r-protein S12/MRPS12/uS12m) are shown in (B,C). Methods: To create panels (A–C), the 2.2-Å cryo-EM human mito-ribosomal structure (Itoh et al., 2021; Itoh et al., 2022) and the structure of the T. thermophilus 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA, tRNA and (PDB Accession number: 4YBB) were superposed with the Matchmaker utility of Chimera X (Pettersen et al., 2021), using protein S12 as a reference chain.