Fig. 4. The acquired cellular changes are rather stable and can be transmitted even when becoming undetectable in the P0-trained generation.
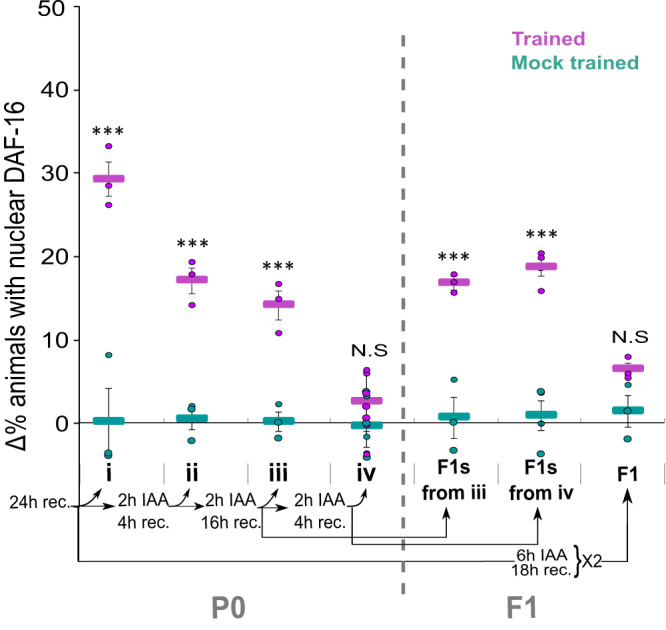
Trained P0-generation animals and their progeny were repeatedly cultivated with the CS IAA in the presence of food. Each such cultivation cycle was followed by a recovery period in the absence of IAA. (i) P0-generation animals showed significant IAA-induced nuclear translocation of DAF-16/FOXO 24 h post training. Trained P0 animals, exposed to IAA once (ii) or twice (iii) in the presence of food, still showed significant IAA-induced responses. These acquired changes were not evident following the third cultivation cycle (iv). F1 progeny of the trained P0 generation, that underwent two (from group iii) or three (from group iv) cultivation cycles of IAA+food, still showed robust IAA-induced responses. F1 animals that underwent two IAA+food cultivation cycles lost the IAA-induced responses. Shown are the means ± SEM of N = 3–7 biologically independent experimental repeats, each scoring ∼50 animals. P-values from left to right: 6.7E−11, 6.6E−5, 2.2E−3, 0.18, 1.1E−4, 6.11E−8, 0.2. ***p < 0.0001 (proportion test, two-sided, Bonferroni correction). Significance comparisons are between trained and mock-trained animals. Source data is provided as a Source Data file.
