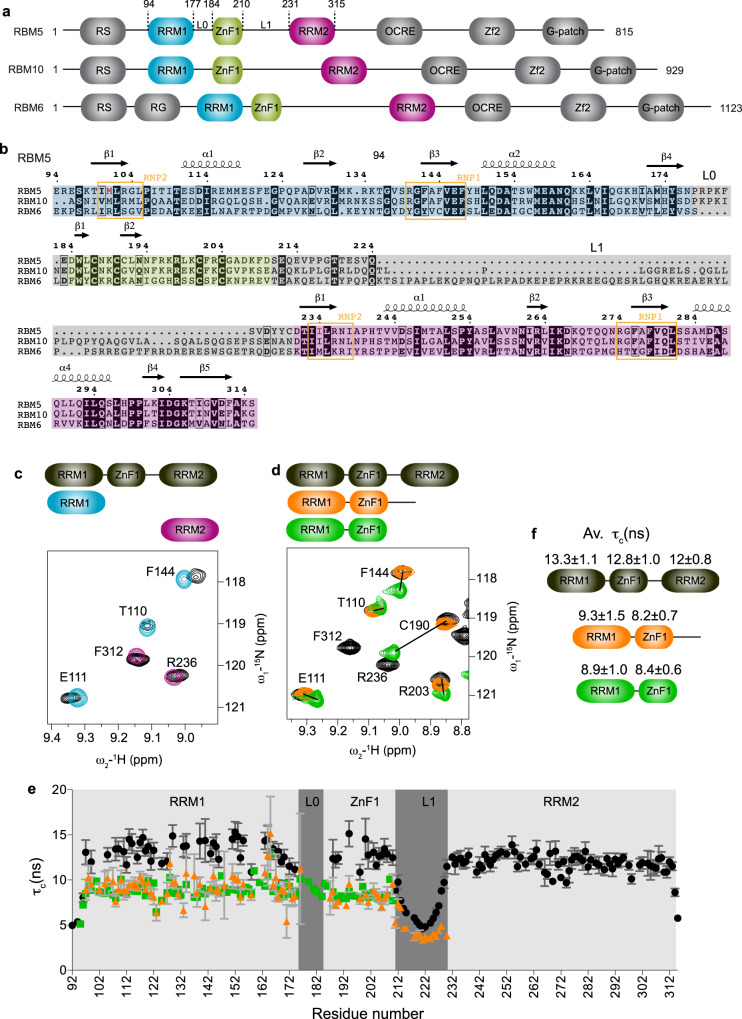
Fig. 1. Structural characterization of RBM5 RRM1-ZnF1 tandem domains.
a Domain organization and b multiple sequence alignment of human RBM5, RBM6, and RBM10 proteins. RNP2 and RNP1 motifs of RRM1 and RRM2 are boxed in orange and domain boundaries of RRM1, ZnF1, and RRM2 are highlighted in blue, green, and pink, respectively. Linkers L0 and L1 connecting RRM1-ZnF1 and ZnF1-RRM2, respectively are highlighted in gray. The non-canonical hydrophobic residues found instead of the canonical aromatic residues in RNP2 motif of both RBM5 RRM1 and RRM2 domains are colored in red. c Overlay of 1H-15N HSQC spectra of three RRM1-ZnF1S-RRM2 domains construct (black) and single RRM1 (light blue) and RRM2 (purple) domains. d Overlay of 1H-15N-HSQC spectra of the three RRM1-ZnF1S-RRM2 domains construct (black) with that of RRM1-ZnF1S-L1 (orange) and RRM1-ZnF1S (green). Zoomed representative residues are shown. e Tumbling correlation time τc values (calculated from the ratio of 15N R2/R1 relaxation rates) are plotted vs. residue number for RRM1-ZnF1S-RRM2 (black), RRM1-ZnF1S-L1 (orange) and RRM1-ZnF1S (green) and their domain-wise average τc values ± SD are indicated in f. Error bars are derived from relaxation data. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.