Fig. 4. HROB promotes DNA unwinding by hexameric MCM8–9.
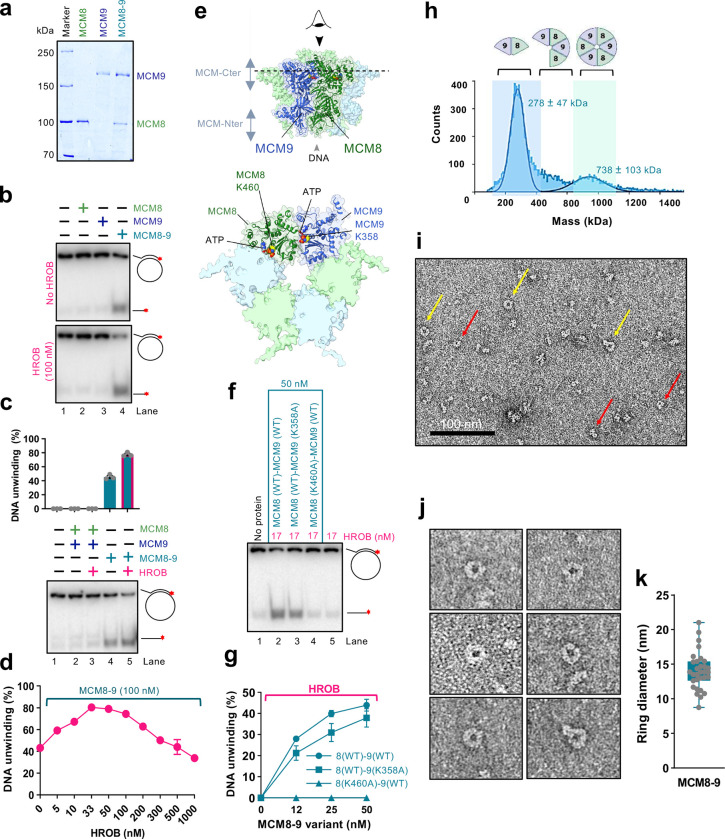
a. Purified wild type human FLAG-MCM8, MBP-MCM9 and FLAG-MCM8-MBP-MCM9 heterodimer complex used in this study.
b. MCM8, MCM9 (single polypeptides, 100 nM) and the MCM8–9 complex (co-expressed, 100 nM) were used in helicase assays with and without HROB (100 nM) using M13-based circular DNA substrate with 21 mM NaCl. The red asterisk indicates the position of the radioactive label. A representative assay is shown.
c. MCM8 and MCM9, combined upon individual expression (lanes 2 and 3) or co-expressed (lanes 4 and 5), all 100 nM, were used in helicase assays with or without HROB (100 nM) using M13-based circular DNA substrate with 21 mM NaCl. The red asterisk indicates the position of the radioactive label. Top, quantification; error bars, SEM; n = 3; bottom, a representative experiment.
d. Quantitation of DNA unwinding experiments by human MCM8–9 in the presence of increasing concentrations of HROB such as shown in Extended Data Fig. 4g. Error bars, SEM; n = 3.
e. AlphaFold2 model depicting the positions of ATPase sites at the interfaces of MCM8 and MCM9 subunits within the hexameric complex. Walker A lysine of MCM8 (K460) and MCM9 (K358) are shown. The lower cartoon represents a view from the C-terminal end of the complex.
f. DNA unwinding by wild type or ATP binding-deficient MCM8–9 variants with HROB, as indicated using M13-based circular DNA substrate with 25 mM NaCl. The red asterisk indicates the position of the radioactive label. A representative assay is shown.
g. Quantification of helicase assays such as shown in panel f. HROB was used at 1/3 concentration of MCM8–9 (nM). Error bars, SEM; n = 3.
h. Measured molecular weight distributions of human MCM8–9 using mass photometry. FLAG-MCM8-MBP-MCM9 was used, corresponding to a theoretical molecular weight of 266 kDa for a heterodimer and 798 kDa for a hexamer. Error, SD.
i. Negative staining transmission electron micrograph of human MCM8–9 (220 nM). Yellow arrows indicate clearly distinguishable top views of MCM8–9 rings, while red arrows denote smaller, less well recognizable rings or side views of rings, which make up the majority of the visible particles. A representative image is shown.
j. Representative transmission electron micrographs of MCM8–9 rings.
k. Quantification of diameter sizes of distinguishable MCM8–9 rings as shown in panel j. Error bars, SD; n = 31.