Figure 4.
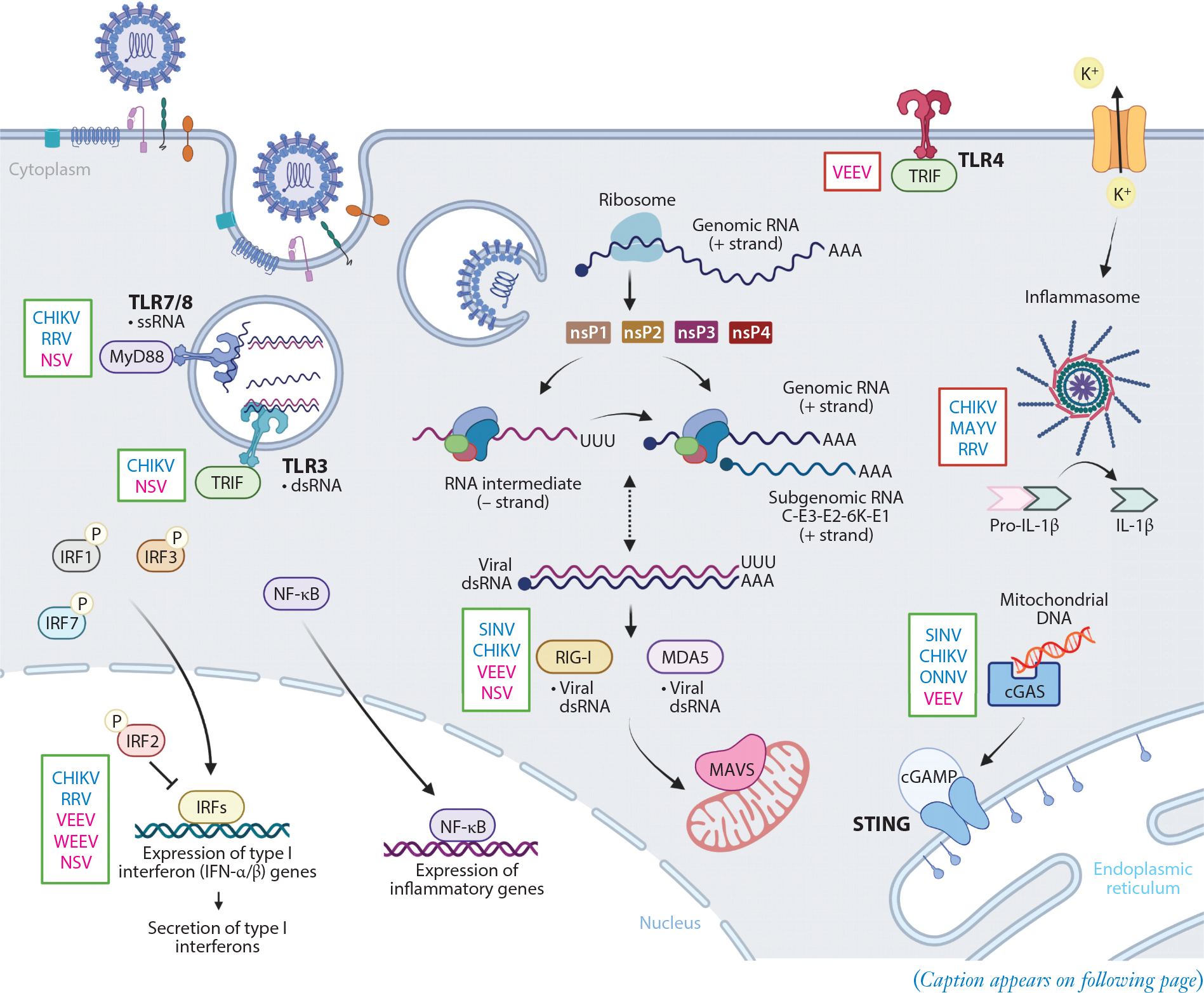
Overview of innate immune signaling pathways impacting alphavirus infection. Alphavirus entry is mediated by attachment factors and receptors at the host cell surface. Once internalized in an endosome, alphaviruses undergo fusion of the viral envelope with the endosomal membrane to release nucleocapsid and positive-strand viral genomic RNA into the cytoplasm. This RNA is translated to generate nonstructural proteins (nsP1–4) that form an initial viral replication complex to synthesize a negative-strand RNA intermediate. The viral replication complex will then switch to generate positive-strand genomic RNA and (positive-strand) subgenomic RNA from these negative-strand RNA intermediates. Subgenomic RNA encodes the structural polyproteins (C-E3-E2–6K-E1), and these are translated and processed in the endoplasmic reticulum before delivery to the cell surface to encapsulate genomic RNA during virion budding. PRRs at the cell surface (TLR4) and within the endosome (TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8) will recognize PAMPs and signal through distinct adaptor proteins (e.g., MyD88 and TRIF). TLR activation, along with secondary signaling through potassium efflux, can activate the inflammasome. Transcription of viral RNA in the cytoplasm leads to formation of dsRNA, which can activate cytoplasmic PRRs, RIG-I and MDA5, to interact with MAVS on the mitochondrial membrane. cGAS can recognize endogenous or foreign DNA released during infection, leading to activation of STING. These recognition events initiate translocation of IRFs and NF-κB into the nucleus and regulation of type I interferons and proinflammatory gene expression. Innate immune pathways that confer presumed protective (green box) or pathological (red box) responses to arthritogenic (blue font) or encephalitic (pink font) alphavirus infection are indicated to the left of each represented signaling molecule. Abbreviations: cGAMP, cyclic GMP-AMP; cGAS, cGAMP synthase; CHIKV, chikungunya virus; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MAYV, Mayaro virus; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NSV, neuroadapted SINV; ONNV, o’nyong-nyong virus; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; RRV, Ross River virus; SINV, Sindbis virus; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TLR, Toll-like receptor, VEEV, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus; WEEV, western equine encephalitis virus. Adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
