Figure 5.
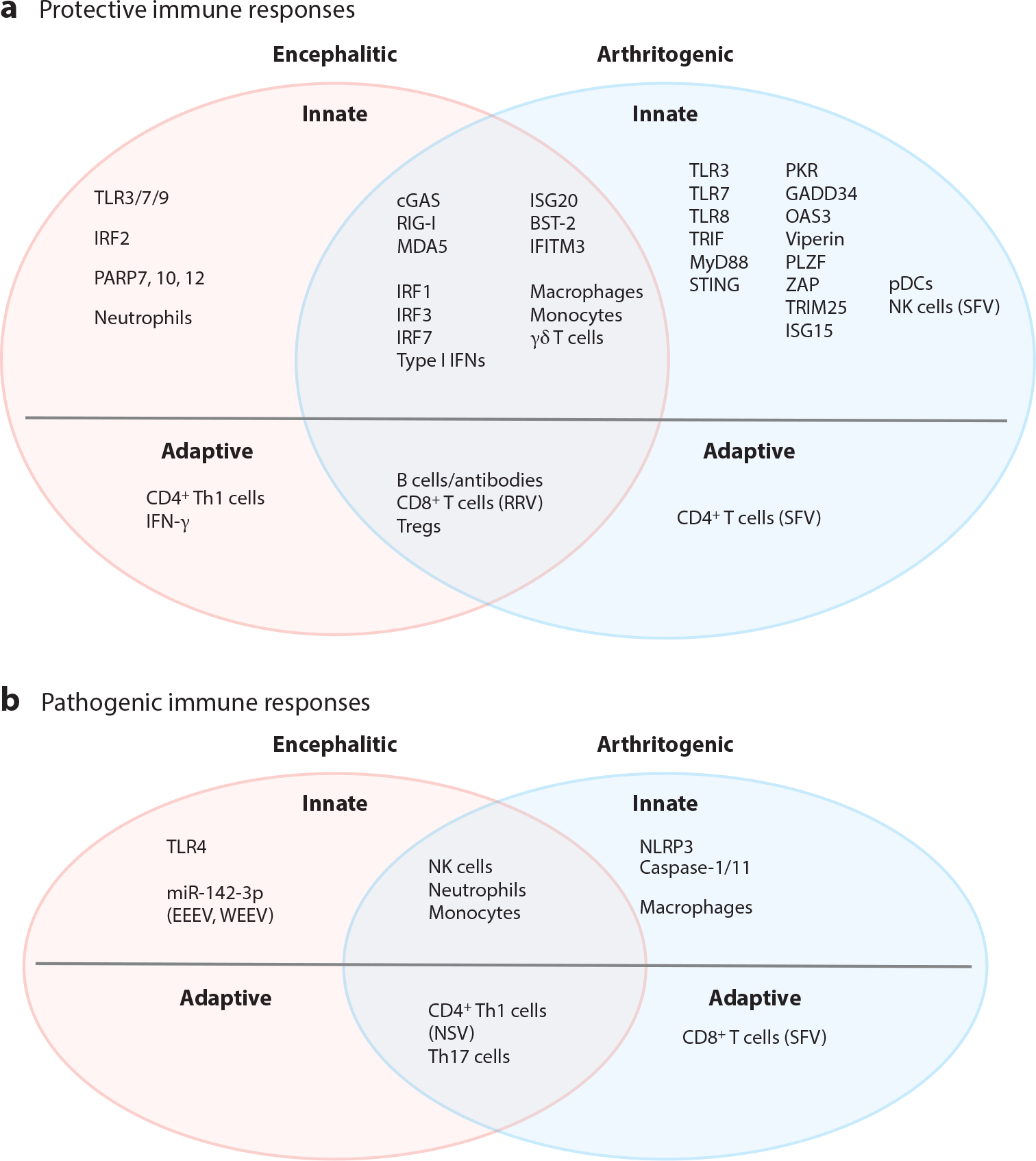
Protective and pathogenic components of the immune response to alphavirus infections. Pattern recognition receptors, type I interferons, interferon-stimulated genes, and immune cells involved in the innate and adaptive immune responses to alphaviruses that are encephalitic (pink ovals), arthritogenic (light blue ovals), or both encephalitic and arthritogenic (mauve overlap) are categorized by their known or presumed (a) protective and/or (b) pathogenic contributions. Specific viruses are indicated when the type of immune response differs compared to other viruses in the respective group. Abbreviations: BST-2, bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; EEEV, eastern equine encephalitis virus; GADD34, growth arrest and DNA damage–inducible protein 34; IFITM3, interferon-induced transmembrane 3; IRF1, interferon regulatory factor 1; ISG20, interferon-stimulated gene 20; NK, natural killer; NSV, neuroadapted Sindbis virus; OAS3, 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase 3; PARP7, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 7; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell; PKR, protein kinase R; PLZF, promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger; RRV, Ross River virus; SFV, Semliki Forest virus; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; Th1, T helper type 1; TLR3, Toll-like receptor 3; Treg, regulatory T cell; TRIM25, tripartite motif-containing 25; WEEV, western equine encephalitis virus; ZAP, zinc finger antiviral protein.
