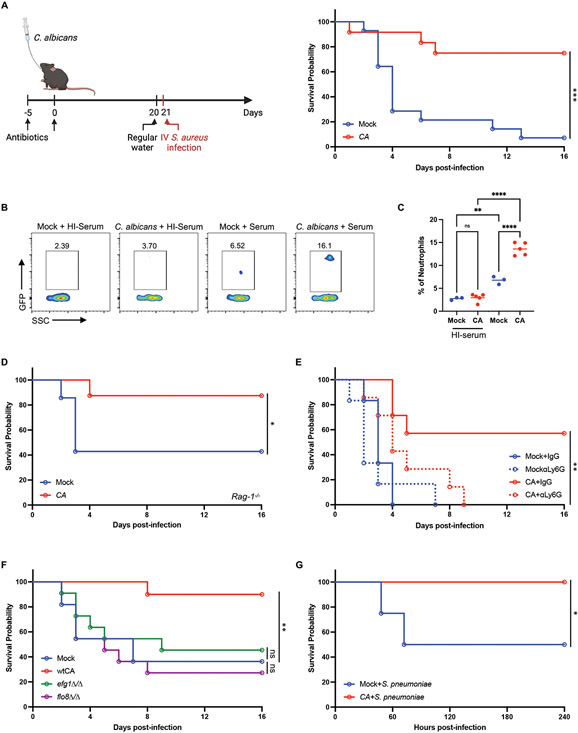
Fig. 6. Intestinal colonization by C. albicans protects against gram-positive bacterial infections.
(A) Survival following i.v. injection of S. aureus on day 21 following PBS (mock, N=14) or C. albicans (N=12) inoculation. Antibiotics-containing water was swapped with regular water 24 hours before S. aureus infection. 3 independent repeats. (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of neutrophils isolated from the BM of mock and C. albicans-colonized mice incubated with GFP-labeled S. aureus together with untreated or heat-inactivated (HI) mouse serum for 20 minutes at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 25. (C) Quantification of frequency of GFP+ neutrophils from (B). N = 3 mock and N = 5 C. albicans-colonized mice. (D) Survival of Rag1−/− knockout mice infected with S. aureus on day 21 after PBS (N=7) or C. albicans (N=8) inoculation. 2 independent repeats. (E) Survival of mice infected with S. aureus on day 21 after PBS or C. albicans inoculation and treated with anti-Ly6G or IgG isotype control antibodies on day −1, 1, 3, 5, and 7 days post-infection. N = 7 mice per group. (F) Survival of mice infected with S. aureus on day 21 after inoculation with PBS, wild-type, or mutant C. albicans (efg1Δ/Δ and flo8D/flo8Δ/Δ). N = 22 mice per group. 2 independent repeats. (G) Survival of mice injected i.p. with S. pneumoniae on day 21 after PBS or C. albicans inoculation. N = 12 mice per group. Dots in bar graphs correspond to individual mice. Mean and SD are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by ordinary one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test (C). (A, D-G) log-rank Mantel–Cox test. ns, not significant.