Figure 1. RBM3 CRISPR knockout screen identifies splicing factors as key RBM3 regulators. See also Fig EV1 .
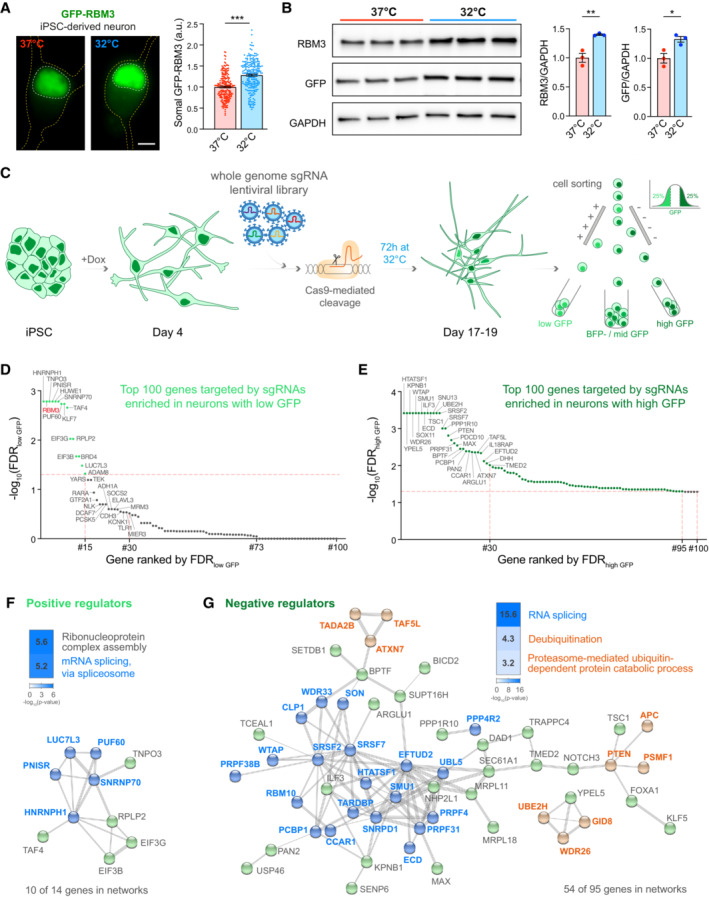
-
ARepresentative images and quantification of somal intensity per unit area of GFP‐RBM3 i‐neurons at 37°C or after 72 h cooling at 32°C. Nuclei and cells are outlined by white and yellow dashed lines, respectively. N = 207 (37°C) and 220 (32°C) cells. Scale bar: 5 μm.
-
BWestern blots and quantification of RBM3 and GFP normalised to GAPDH in GFP‐RBM3 i‐neurons at 37 or 32°C (72 h).
-
CSchematic of experimental steps in RBM3 CRISPR screen in i‐neurons. GFP‐RBM3 iPSCs stably expressing Cas9 after 4 days of Dox‐induced differentiation are transduced with a whole‐genome lentiviral sgRNA library expressing a BFP reporter. 10–12 days after transduction, the i‐neuron cultures are incubated at 32°C for 72 h, followed by FACS to sort BFP‐positive i‐neurons with the highest and lowest 25% GFP fluorescence intensity into separate pools. N = 2 GFP‐RBM3 clones and 3 biological replicates.
-
D, ETop 100 RBM3 positive regulator candidates with their sgRNAs enriched in the low‐GFP i‐neuron pool (D). Top 100 RBM3 negative regulator candidates with their sgRNAs enriched in the high‐GFP i‐neuron pool (E). Genes ranked by statistical significance (FDR). Horizontal dashed line: FDR = 0.05.
-
FThe top‐ranked Gene Ontology terms and STRING networks of 14 positive regulator candidates (FDR <0.05, RBM3 is excluded). Genes related to RNA splicing are indicated in blue.
-
GThe top‐ranked Gene Ontology terms and STRING networks of 95 positive regulator candidates (FDR <0.05). Genes related to RNA splicing are coloured in blue. Genes involved in deubiquitination or proteasome‐mediated ubiquitin‐dependent protein catabolic processes are coloured in orange.
Data information: N = 3 biological replicates. Mean ± SEM; *(P < 0.05), **(P < 0.01), ***(P < 0.001); unpaired t‐tests in (A) and (B).
Source data are available online for this figure.
