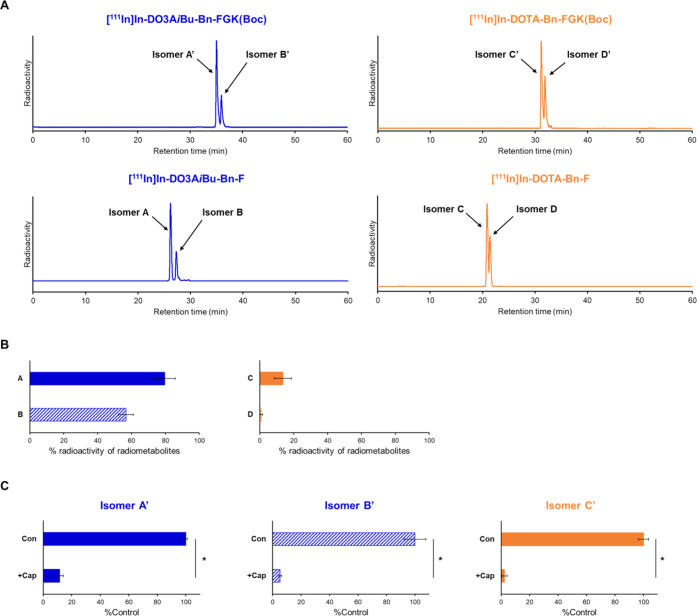
Figure 3.
(A) Radiochromatograms of 111In-labeled LMW substrates and the authentic radiometabolites liberated from the LMW substrates by the action of ACE on the renal BBM. Two peaks were observed for each radiochromatogram and identified as isomers by mass spectrometry of the corresponding nonradioactive In-labeled LMW substrates. (B) Liberation of radiometabolites after incubation of 111In-labeled LMW substrates with BBM vesicles for 2 h. The protein concentrations of BBM vesicles were 1 mg/mL for [111In]In-DO3AiBu-Bn-FGK(Boc) and 10 mg/mL for [111In]In-DOTA-Bn-FGK(Boc). Isomers from [111In]In-DO3AiBu-Bn-FGK(Boc) and [111In]In-DOTA-Bn-FGK(Boc) were recognized by enzymes on the BBM vesicles to liberate the respective radiometabolite. (C) Liberation rates of radiometabolites in the absence (Con) or presence of an inhibitor for ACE, captopril (+Cap). Significances were determined by Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05). The results indicated that ACE was involved in the cleavage of the FGK linkages.