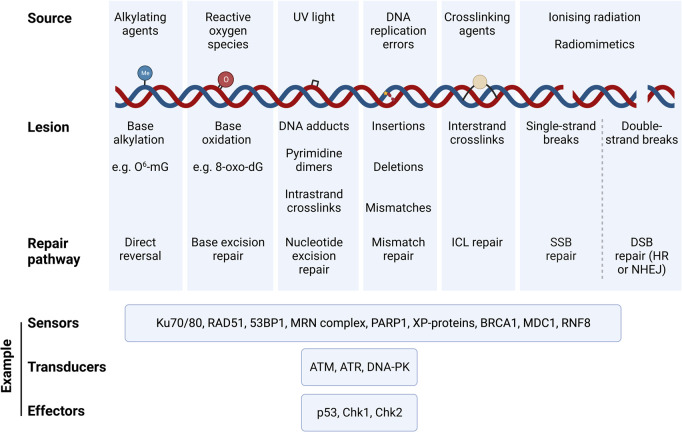
FIGURE 1.
Types of DNA damaging agents, resulting lesions and canonical repair pathways that correct them. DNA experiences a variety of genotoxic insults from both endogenous and exogenous sources. These result in specific lesions that can be repaired via specific DNA repair pathways that are triggered by the DNA damage response (DDR). Damaged DNA is sensed, signalled, and repaired through a cascade of signalling mechanisms elicited by DNA sensors, tranducers, and effectors, which are specific to the DNA lesion type and repair pathway. Examples of such DDR proteins are illustrated. Abbreviations: O6-mG, O-6-methylguanine; 8-oxo-dG, 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine; ICL, interstrand crosslink; HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; 53BP1, p53·-binding protein 1; MRN complex, Mre11/Rad50/Nbsl; PARP1, Poly [ADP-ribose] Polymerase 1; XP-proteins, Xeroderma Pigmentosum proteins; BRCA1, breast cancer gene 1; MDC1, Mediator of DNA Damage Checkpoint 1; RNF8, Ring Finger Protein 8; ATM, Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated; ATR, Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-related; DNA-PK, DNA Protein Kinase complex; Chk1, Checkpoint Kinase 1; Chk2, Checkpoint Kinase 2.