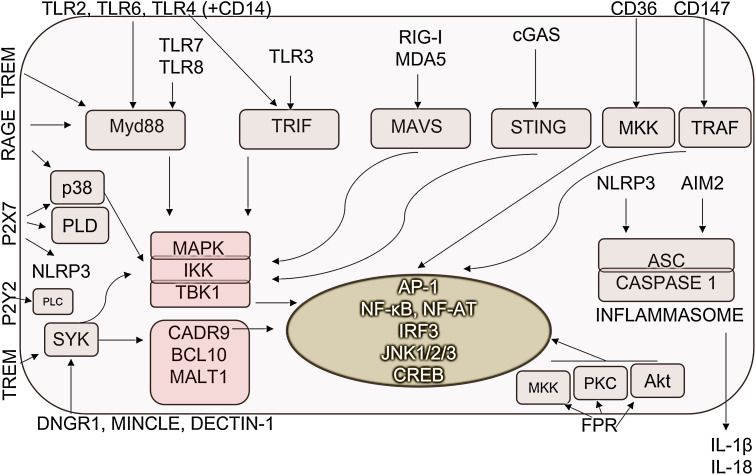
Figure 3.
DAMP-sensing receptor-induced signaling pathways. DAMPs are recognized by pathogen-recognition receptors as well as various receptors specialized for the detection of human molecules. Their detection dominantly resulted in the activation of inflammation-promoting signaling pathways and transcription factors. AP-1, Activator protein 1; ASC, Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; CD, cluster of differentiation; CREB, Cyclic AMP,Responsive Element-Binding Protein; DNGR-1, dendritic cell NK lectin group receptor-1; IKK, IκB kinase; JNKs- c,Jun N-terminal kinases; MAPKs, Mitogen-activated protein kinases; MALT1, mucosa-associated-lymphoid-tissue lymphoma-translocation gene 1; MAVS, Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; Mincle, Macrophage Inducible C-Type Lectin; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MYD88, Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-AT, Nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, Phospholipase C; PLD, Phospholipase D; RAGE, Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; STING, Stimulator of interferon genes; SYK, Spleen tyrosine kinase; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRAF, TNF receptor-associated factor; TREM1/2, Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells ½; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β.