Figure 1.
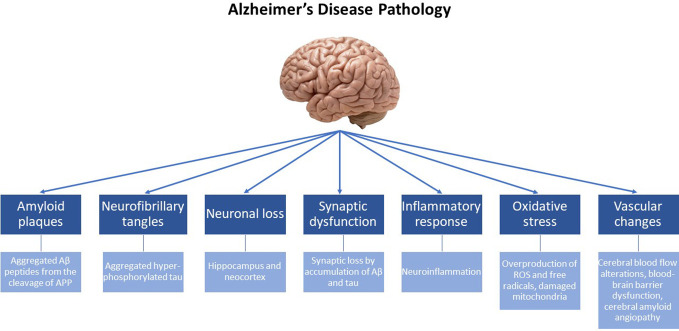
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory impairment. The underlying pathological changes in the brain of individuals with AD include the following key features: Amyloid plaques: Extracellular deposits of beta-amyloid protein (Aβ) form amyloid plaques. These plaques are composed of aggregated Aβ peptides derived from the cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Neurofibrillary tangles: Intracellular neurofibrillary tangles are formed by the hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau protein. In healthy neurons, tau helps maintain the structural integrity of microtubules, but in AD, abnormal tau protein forms twisted filaments, leading to the formation of tangles. Neuronal loss: AD is associated with significant neuronal loss, particularly in brain regions involved in memory and cognitive functions, such as the hippocampus and neocortex. Neuronal loss contributes to the progressive decline in cognitive abilities. Synaptic dysfunction: Synaptic loss and dysfunction occur early. Disruptions in the communication between neurons impair memory formation and retrieval. Synaptic loss is believed to be caused by the accumulation of Aβ and tau pathology. Inflammatory response: AD is characterized by chronic neuroinflammation. Activated microglia and astrocytes are observed in affected brain regions, releasing pro-inflammatory molecules that contribute to neuronal damage. Oxidative stress: The increased production of free radicals and ROS, along with the overexpression of prooxidant enzymes and the dysfunction of mitochondria, contribute to chronic oxidative stress observed in the brain, that is intertwined with chronic neuroinflammation. Vascular changes: Vascular abnormalities are frequently observed in AD. Cerebral blood flow alterations, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and the accumulation of vascular deposits, known as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, are seen in affected individuals.