Figure 1.
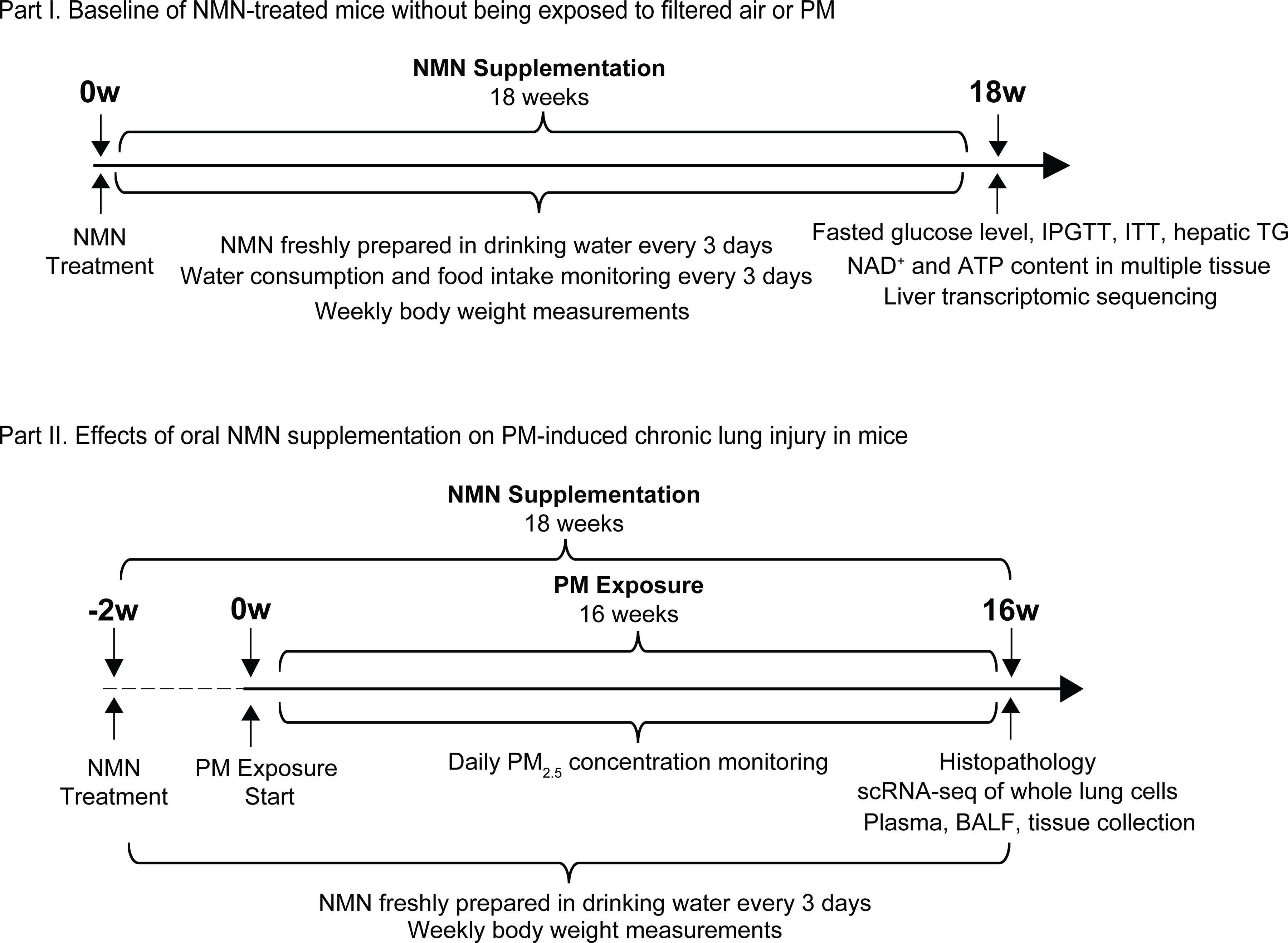
A schematic diagram illustrates the experimental design in this study. The experiment was conducted in two parts: Part I, Characterization of metabolic alterations in mice receiving 18-wk NMN supplementation; and Part II, Effects of NMN supplementation on PM exposure-induced chronic lung injury (NMN supplementation started 2 wk prior to 16-wk PM exposure). Note: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; IPGTT, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance testing; ITT, insulin tolerance testing; , nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; PM, particulate matter; scRNA-seq, single-cell RNA transcriptomic sequencing; TG, triglyceride.
